Quick Leads
Complete PCB Repair Guide: Troubleshooting, Fixing & Preventing Issues for Beginners & Experts

Introduction
PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) are the heart of many electronic devices, and when they fail, it can be a nightmare to troubleshoot and repair.
Without the right knowledge and tools, PCB repairs can be overwhelming, causing delays and even costly replacements.
In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the essential steps to troubleshoot and repair your PCB, ensuring it’s restored to full functionality—whether you’re a beginner or an expert.
How Do You Troubleshoot and Repair a PCB?
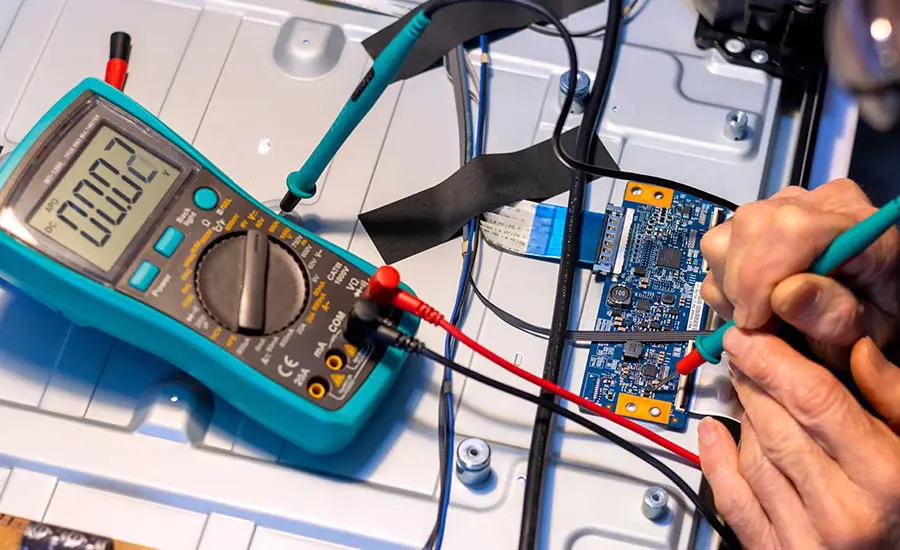
To troubleshoot a PCB, start by mapping out the circuit board and visually inspecting all components for damage like burnt traces or broken parts. Use a multimeter to check for shorts or open circuits, and compare the damaged PCB with an identical one. Once you’ve isolated the faulty components, test integrated circuits and the power supply to identify the issue. Finally, use advanced techniques like signal probing to further diagnose complex problems. Once identified, repairing the PCB often involves replacing or soldering damaged components, and in some cases, using epoxy or Kapton tape to secure new parts. A thorough understanding of PCB layouts and circuitry is essential to successful repair.
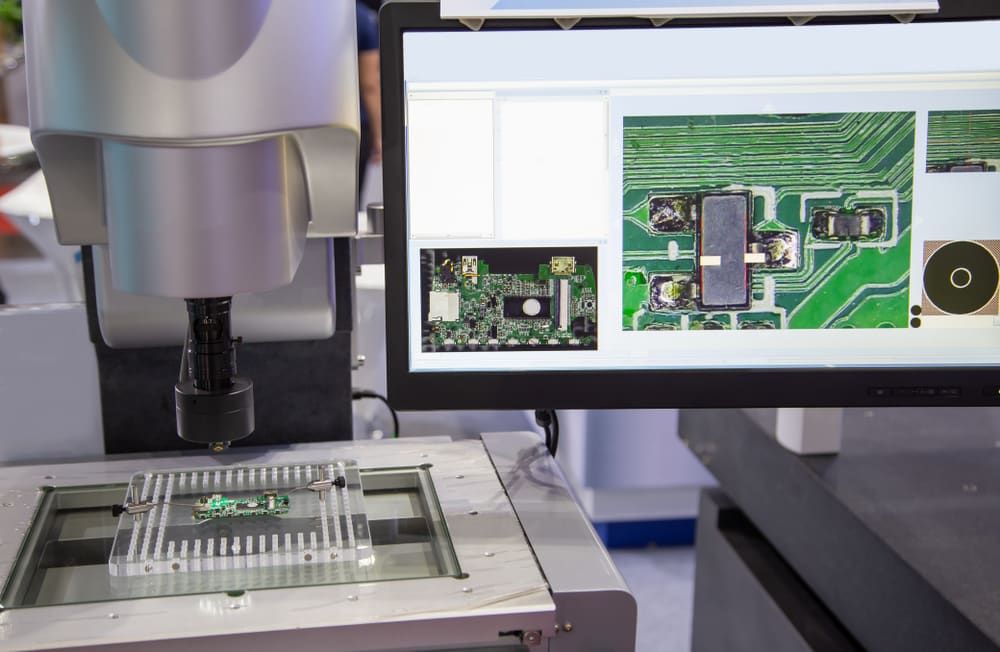
What Is Quality Control in PCB Manufacturing?

What Are the Typical Causes of PCB Damage?
Quality control (QC) is the cornerstone of high-quality PCB production. In the manufacturing process, several steps ensure that each PCB meets strict industry standards before it leaves the factory floor.
The QC process involves:
- Visual Inspections: Automated systems and human inspectors carefully examine the PCB for obvious defects like damaged pads, missing components, or broken traces.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Machines scan the PCBs for soldering issues, misalignments, or component misplacements.
- Electrical Testing: After assembly, PCBs undergo electrical testing to ensure all components are working correctly.
By ensuring high standards during production, manufacturers aim to minimize the chances of faulty PCBs reaching the market, although damages can still occur post-manufacturing.
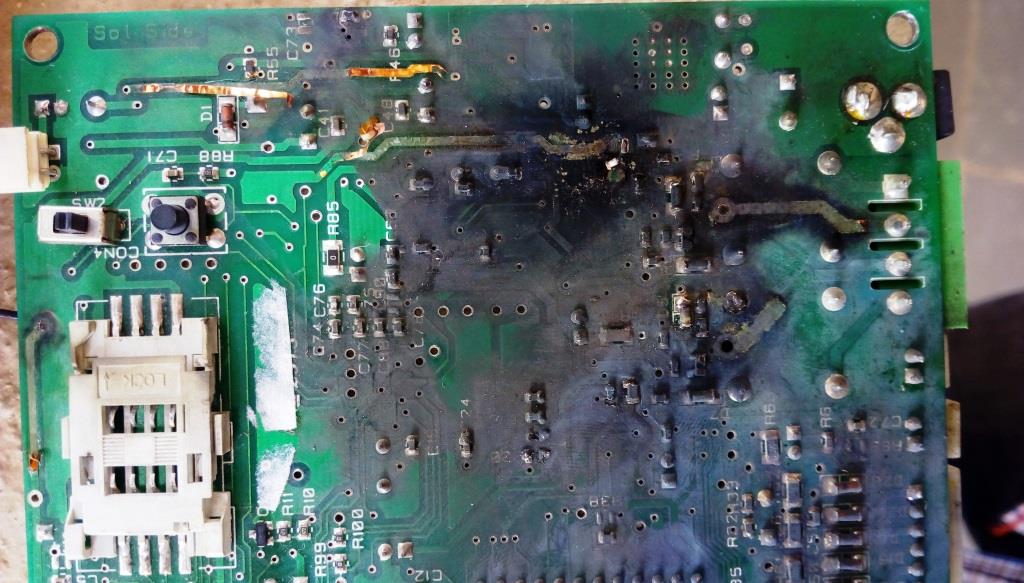

PCBs are prone to various types of damage, whether during manufacturing or in the field. The common culprits include:
- Overvoltage: Too much voltage can damage components and cause them to fail.
- Overheating: Prolonged heat exposure can degrade solder joints and cause components to malfunction.
- Physical Damage: Accidental impacts, bending, or pressure on the PCB can cause cracks or fractures.
- Environmental Factors: Moisture, humidity, and corrosive environments can lead to trace corrosion or component failure over time.
- Manufacturing Defects: Mistakes made during assembly, such as improper soldering or component misplacement, can lead to premature failure.
Understanding these factors helps in troubleshooting and repairing PCBs more efficiently.
How to Troubleshoot a PCB: A Step-by-Step Process

Troubleshooting a PCB can be a systematic process, starting with visual inspection and progressing to more detailed electrical tests. Here’s how to approach it:
- Visual Inspection: Start by examining the PCB for physical damage, such as burnt areas, broken traces, or loose components.
- Use a Multimeter: Check the PCB for shorts and open circuits. A multimeter will help you identify whether the PCB has a connection issue or if certain components have failed.
- Compare to a Working Model: If possible, compare the damaged PCB to a working one. This can help you spot any discrepancies, such as missing components or broken traces.
- Isolate the Defective Component: Once you’ve identified an area of concern, focus on isolating the faulty component, whether it’s a damaged resistor, capacitor, or an integrated circuit.
- Advanced Diagnostics: For more complex issues, use techniques such as signal probing or analyzing the power supply to identify where the fault lies.
Learn how to test your PCB for reliability before installation in our PCB testing guide.
Essential PCB Repair Tools for Beginners and Professionals
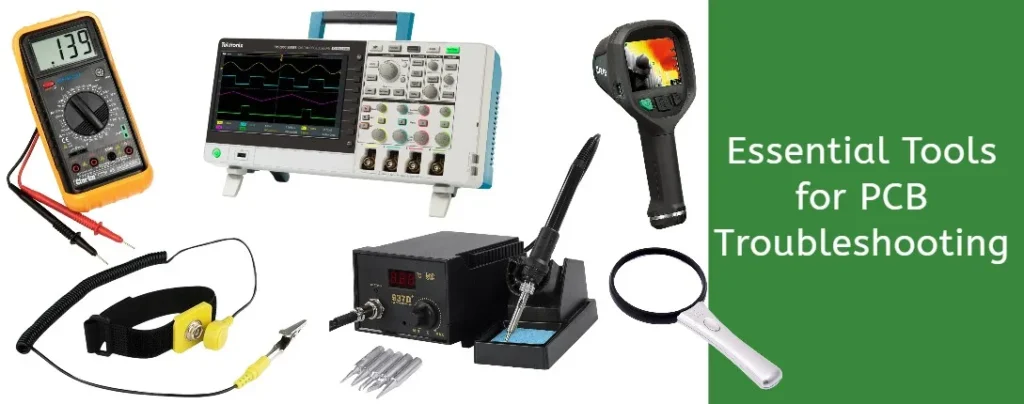

Both beginners and professionals need specific tools to successfully repair a PCB. These tools are essential for both beginners and professionals to troubleshoot PCB problems.Find reliable oscilloscopes and hot air rework stations on Digi-Key or Mouser Electronics For beginners, understanding the basics of PCB troubleshooting can make repairs more efficient. Here’s a breakdown of essential tools:
For Beginners:
- Multimeter: For continuity testing and checking for shorts.
- Soldering Iron: A must-have for basic soldering tasks.
- Desoldering Pump: Helps remove excess solder during repairs.
- Magnifying Glass: For inspecting small components and connections.
- Soldering Wire: For adding new solder to connections.
For Professionals:
- Oscilloscope: Used for advanced signal analysis, helping diagnose issues in high-frequency circuits.
- Signal Generator: Useful for testing the signal flow on the board.
- Hot Air Rework Station: Essential for removing and replacing surface-mounted components.
- Precision Tweezers: For handling tiny components safely.
- PCB Fixture: To hold the board steady during repair.
Looking for the best soldering practices? Explore our guide to common soldering mistakes and how to avoid them.
What Safety Precautions Should You Take During PCB Repair?

When working on PCBs, safety should always be your top priority. Here are some crucial precautions to follow:
- Wear Safety Glasses and Gloves: Protect yourself from hot tools and solder splashes.
- Ventilate Your Workspace: Always work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes from soldering.
- Antistatic Mats and Wristbands: These prevent electrostatic discharge (ESD) from damaging sensitive components on the PCB.
- Work Slowly and Carefully: Rushing can result in damaged components or injury. Always take your time and handle the PCB gently.
How to Fix Damaged PCB Traces and Repair Printed Circuit Boards

Once you’ve identified the issue, the repair process begins. Here’s how to fix damaged PCB traces and other common problems:
- Identify the Faulty Components: Whether it’s a burned-out resistor or a damaged capacitor, figure out what’s broken.
- Desolder the Damaged Parts: Use a soldering iron and desoldering pump to carefully remove the faulty components.
- Replace with New Components: Solder in the new components, ensuring they are correctly placed.
- Repair Traces: If traces are damaged, use wire to bridge the gap or apply PCB repair kits for more serious damage.
- Test the Board: After the repair, test the board to ensure it functions correctly.
Tips to Prevent PCB Failures
Preventing PCB failures is possible with proper care and design. Preventing common PCB failures during manufacturing involves careful design and high-quality testing procedures. Using reliable materials can significantly reduce failures. Read more about selecting durable materials for PCBs on Electronics Weekly.Here are some tips:
- Proper Design: Ensure the PCB design is optimized for power distribution, heat dissipation, and component placement.
- Use High-Quality Components: Choosing high-quality, durable components reduces the risk of failures.
- Regular Testing: Perform routine testing to identify any potential issues early.
- Soldering Techniques: Use proper soldering techniques to avoid damaging components or creating shorts.
Proper design and testing are crucial. Check out our comprehensive guide on PCB design tips to prevent failures from the start.
Limited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
Claim your $100 discount now – this offer won’t last long! Today ONLY!
Don’t miss this chance to save on your next project.
[Hurry! Only 50 discounts remaining!]
 Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide
Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide No hidden fees – transparent pricing
No hidden fees – transparent pricing Guaranteed quality with on-time deliver
Guaranteed quality with on-time deliverConclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the essential steps to troubleshoot and repair your PCB, from understanding the manufacturing process to using the right tools and safety precautions. Whether you’re a beginner or an expert, mastering these techniques will ensure you can confidently address any PCB failure. Remember, preventing future failures starts with proper PCB design, high-quality components, and ongoing maintenance.
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




