Quick Leads
How to Design Start-Stop Circuits for Automated Systems
Introduction
Designing reliable and efficient start-stop circuits is a big deal when you’re building automated systems. Whether you’re designing a motor control circuit, a relay-based system, or implementing a PLC-controlled start-stop sequence, you need to carefully select components and wire everything together to make it work. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the key things you need to know about designing start-stop circuits for automation systems. We’ll talk about the different types, the parts you need, how to wire everything up, and how to troubleshoot it.
What is a Start-Stop Circuit?
Start-stop circuits are a big deal when it comes to controlling machinery, especially in automated systems where safety, reliability, and efficiency are key. These circuits are made up of simple components like push buttons, relays, and contactors that work together to start or stop a machine or process.

Types of Start-Stop Circuits
Start-stop circuits come in different forms, each with its own set of components and functions. The most common types include:
-
Push-Button Start-Stop Circuits A basic design where a start button initiates the process, and a stop button halts it.
-
Relay-Based Start-Stop Circuits :A relay-based system gives you more flexibility because it keeps the current flowing even after you let go of the start button. That makes it perfect for motor control.

3. PLC-Controlled Start-Stop Circuits: More advanced systems that integrate a PLC for controlling the start-stop sequence and offering remote control, diagnostics, and automation flexibility.
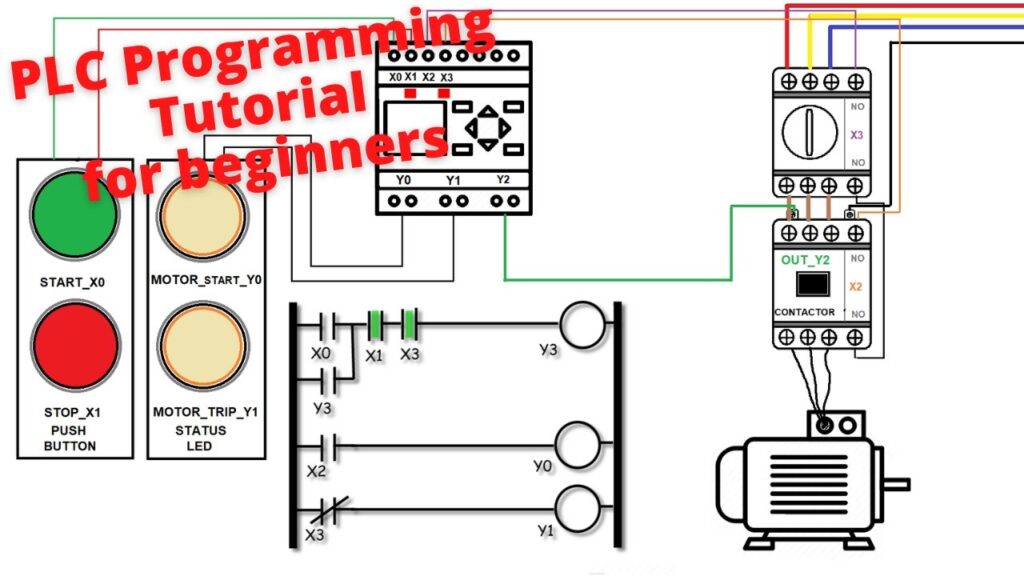
Key Components of Start-Stop Circuits
The components you select for your start-stop circuit depend on the type of system you’re designing. Here’s a look at some common components:
-
Push Buttons: Used for manual start/stop operations.
-
Relays: Used to control large currents and to maintain circuit flow after the start button is released.
-
Contactors: Switches that control the motor or equipment when activated by the relay.
-
Fuses and Circuit Breakers: Provide protection against overcurrent or short circuits.
-
Power Sources: Ensure proper voltage and current for the system to operate correctly.
Wiring and Connection
Wiring plays a critical role in the proper functioning of a start-stop circuit. You want to wire your components correctly so that you don’t have any interference or loss of power. Always follow electrical standards and safety protocols during installation.
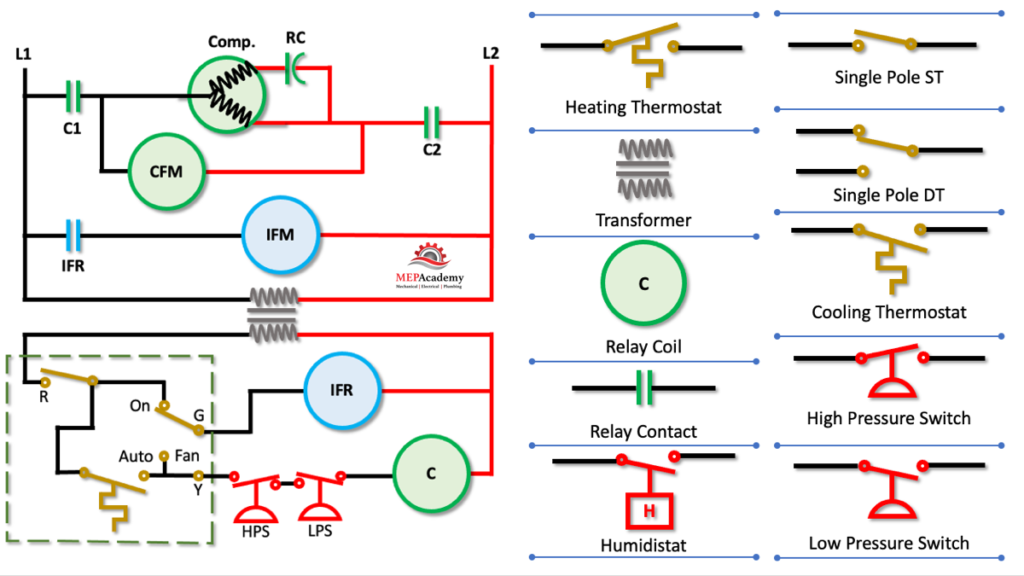
Designing Start-Stop Circuits
Designing a start-stop circuit involves several key steps to ensure the system operates smoothly and safely.
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
Understand the needs of the automated system. For instance, do you need a simple push-button control, or will you require a PLC-based system for more complex applications?
Step 2: Select Components
Pick your parts based on how much power you need, how many control inputs and outputs you need, and what safety standards you need to meet.
Step 3: Wiring the Circuit
Make sure you use the right size wire, and put in fuses or circuit breakers to keep from burning up your stuff..
Step 4: Testing
After wiring, test the system thoroughly to ensure it starts and stops as expected and that safety features are functional.
Applications of Start-Stop Circuits in Automated Systems
Start-stop circuits are used in a wide range of industries, from simple manufacturing lines to complex robotic systems.. For example:
Manufacturing Lines: Start-stop circuits control machinery, ensuring that operations run smoothly and safely.
Robotics: Robots rely on start-stop circuits for precise motor control.
HVAC Systems: These circuits start and stop equipment in automated heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
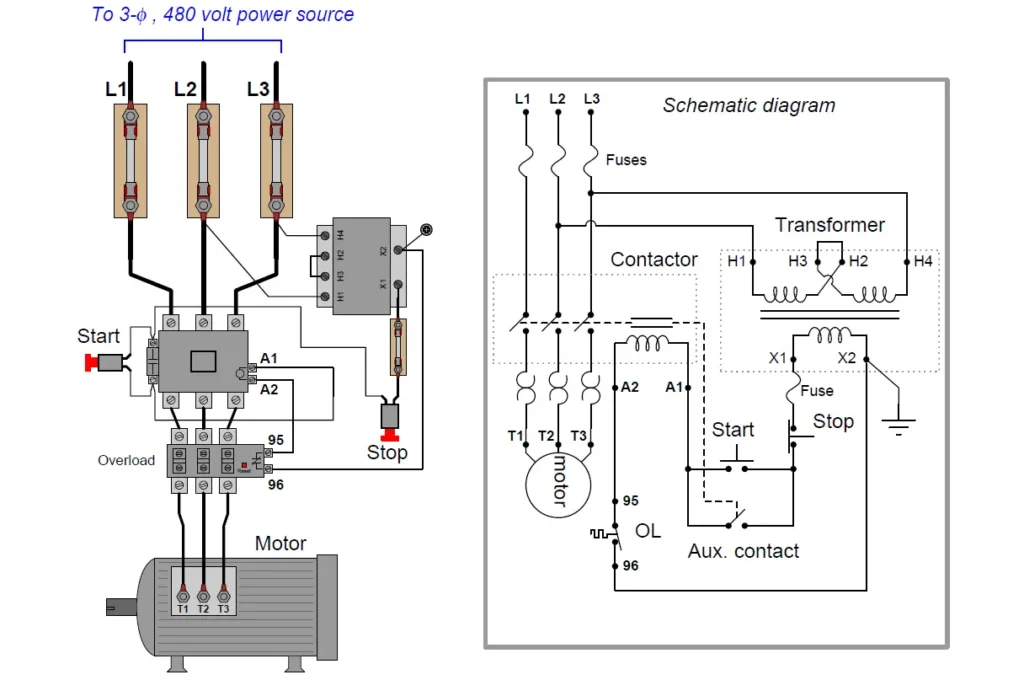
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Start-Stop Circuits
Start-stop circuits can face issues like unresponsive buttons, power interruptions, or faulty relays. Troubleshooting these issues quickly is essential for minimizing downtime in automated systems.
-
Problem: The motor doesn’t start when the button is pressed.
-
Solution: Check for a broken connection or a faulty relay.
-
-
Problem: The system doesn’t stop when the button is pressed.
-
Solution: Inspect the stop button and check for mechanical failure or wiring issues.
-
Safety Features in Start-Stop Circuits
When designing start-stop circuits, it’s vital to include safety mechanisms to prevent accidents. Safety features might include emergency stop buttons, interlock switches, and overload protection.
-
Emergency Stop Buttons: Provide a quick shutdown option in case of emergencies.
-
Interlock Switches: Prevent operation unless all conditions are safe.
-
Overload Protection: Prevents the motor or circuit from overheating.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
You need push buttons, relays, contactors, and fuses to make a start-stop circuit work.
Start by inspecting the power supply, checking the relays, and testing the wiring for any faults.
Relay-based circuits are simpler. You use mechanical relays to turn things on and off. PLC-controlled circuits are more flexible. You can do more stuff with them.
The key components include push buttons, relays, contactors, fuses, and circuit breakers.All these parts work together to turn a motor or system on and off in a factory.
PLC-controlled start-stop circuits are more flexible and programmable, so you can do more stuff with them. Relay-based start-stop circuits are simpler. You use relays to turn things on and off.
Limited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
 Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide
Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide No hidden fees – transparent pricing
No hidden fees – transparent pricing Guaranteed quality with on-time deliver
Guaranteed quality with on-time deliverConclusion
You need to know how to design a good start-stop circuit if you want to make things work right and safe in factories all over the world. Whether you’re using push buttons, relays, or fancy PLCs, you need to know the parts and how to put them together so you can make your system work better and safer.. Ready to optimize your automated system?
Contact us for expert advice on designing custom start-stop circuits tailored to your needs!
Key Takeaways:
Understanding Start-Stop Circuits: Start-stop circuits are what you use to turn things on and off. They’re used in motor control applications.
Types of Circuits: There are three types of start-stop circuits: push-button, relay-based, and PLC-controlled.
Critical Components: The parts you need for a start-stop circuit are push buttons, relays, contactors, and circuit breakers.
Design Considerations: When you’re designing a start-stop circuit, you have to pick the right parts, wire it correctly, and make sure it doesn’t fail.
Troubleshooting and Safety: If you want your start-stop circuit to last a long time, you have to troubleshoot it, follow safety rules, and do maintenance.
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




