Quick Leads
Choosing between Lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery packs and Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) battery packs can be challenging, especially when considering factors like energy density, battery lifespan, self-discharge rate, temperature resistance, cost, and best applications.
Whether you’re selecting a rechargeable battery for electronic devices, electric vehicles (EVs), or industrial applications, understanding the key differences between Lithium vs NiMH batteries is crucial.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down:
✅ Which battery lasts longer: Lithium or NiMH?
✅ Which battery is better for high-performance applications?
✅ Is NiMH more cost-effective than Lithium-ion in the long run?
✅ Which battery type is more eco-friendly?
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of NiMH vs Lithium battery pros and cons and know exactly which battery is best for your specific needs.

Lithium vs NiMH: What’s the Key Difference?
1. Energy Density: Which Battery Packs More Power?
Energy density measures how much power a battery can store relative to its size and weight. This factor is crucial for portable electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and industrial applications where space and weight constraints play a significant role.
🔋 Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery: High Energy Density for Compact Devices
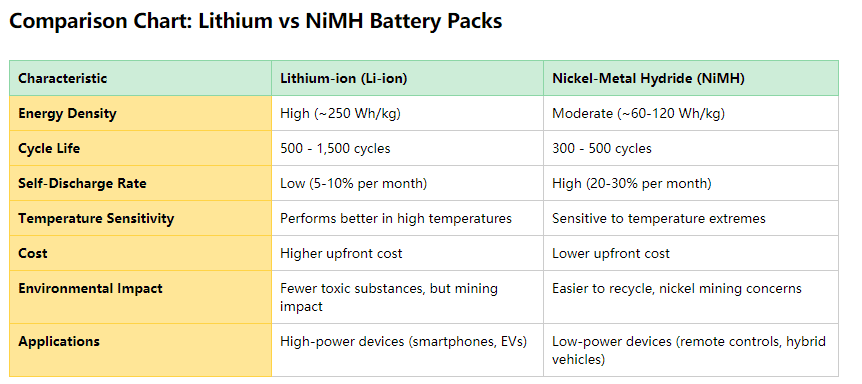
✅ Higher energy density – Li-ion batteries offer an average of 250 Wh/kg, making them significantly more efficient than NiMH.
✅ Lightweight & compact – Their high energy-to-weight ratio makes them ideal for smartphones, laptops, power tools, and EV battery packs.
✅ Preferred for high-performance applications – Due to their superior energy storage capabilities, Li-ion batteries are commonly used in electric cars (Tesla, Nissan Leaf), medical devices, and aerospace applications.
🔋 Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery: Bulkier & Heavier for the Same Power
🚫 Lower energy density – NiMH batteries provide only 60-120 Wh/kg, meaning they need to be larger and heavier to store the same energy as a Li-ion battery.
🚫 Less suitable for weight-sensitive applications – Due to their bulkier size, NiMH batteries are rarely used in mobile phones, tablets, or modern EVs.
✅ More common in household rechargeable batteries – NiMH batteries are still widely used in AA/AAA rechargeable batteries, cameras, and hybrid vehicles like the Toyota Prius.
🏆 Conclusion: Which Battery Has Better Energy Density?
When it comes to energy storage efficiency, Lithium-ion batteries are the clear winner. Their higher power-to-weight ratio, lightweight design, and compact size make them the best choice for portable electronics, electric cars, and high-performance industrial applications.
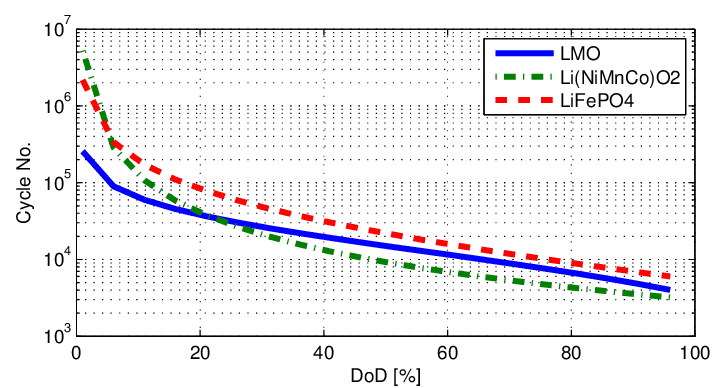
2. Cycle Life: Which Battery Lasts Longer?
The cycle life of a battery refers to how many charge and discharge cycles it can undergo before its capacity degrades significantly. A longer cycle life means fewer replacements and better long-term cost efficiency, making it an essential factor for electric vehicles (EVs), power tools, and industrial applications.
🔋 Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery: Longer Lifespan & Durability
✅ Higher cycle life – Li-ion batteries typically last between 500 to 1,500 charge cycles, depending on battery type and usage conditions.
✅ Better longevity – Many high-quality Li-ion cells (such as those used in Tesla batteries or medical devices) can last up to 2,000 cycles with proper care.
✅ Ideal for high-use applications – Smartphones, laptops, EV battery packs, and solar energy storage benefit from Li-ion’s longer lifespan.
🔋 Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery: Shorter Lifespan, More Frequent Replacements
🚫 Lower cycle life – NiMH batteries typically last between 300 to 500 cycles, meaning they require more frequent replacements.
🚫 Not ideal for daily heavy use – Devices that frequently charge and discharge (such as electric tools, hybrid vehicles, and industrial equipment) may experience faster wear.
✅ Still useful for low-power devices – NiMH batteries are often found in cordless phones, cameras, and household rechargeable batteries where longevity is less critical.
🏆 Conclusion: Which Battery Lasts Longer?
If you need a long-lasting rechargeable battery with fewer replacements over time, Lithium-ion batteries are the better choice. Their higher cycle life and slower degradation make them ideal for electric vehicles, high-performance gadgets, and industrial applications where durability matters.
4. Temperature Sensitivity: Which Battery Performs Better in Extreme Conditions?
Both Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries and Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries are affected by temperature fluctuations, but they perform differently under extreme heat and cold conditions.
🔋 Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery: Better High-Temperature Performance
✅ Handles heat better – Li-ion batteries perform well in higher temperatures compared to NiMH, making them ideal for hot climates and high-temperature applications.
🚫 Heat degradation over time – While they tolerate heat better, prolonged exposure to extreme heat (above 45°C / 113°F) can accelerate capacity degradation and potentially lead to battery failure.
✅ Used in extreme environments – Many electric vehicles (EVs), industrial power systems, and aerospace applications use Li-ion due to its thermal stability.
🔋 Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery: More Sensitive to Temperature Extremes
🚫 Cold weather issues – NiMH batteries lose charge quickly in cold temperatures (below 0°C / 32°F), reducing their effectiveness in winter conditions.
🚫 Heat-related capacity loss – Excessive heat can cause faster capacity degradation and, in some cases, battery leakage.
✅ Still useful in controlled environments – NiMH batteries work well in moderate climates and are commonly found in household rechargeable batteries, hybrid cars, and low-power applications.
🏆 Conclusion: Which Battery Handles Temperature Changes Better?
For applications requiring temperature stability, Lithium-ion batteries are the better choice. Their higher tolerance to heat makes them suitable for hot climates, outdoor devices, and electric vehicles, whereas NiMH batteries struggle in extreme conditions.
5. Cost: Which Battery Offers the Best Long-Term Value?
The cost of a battery is an important factor, especially in cost-sensitive applications like consumer electronics, renewable energy storage, and electric vehicles (EVs). While NiMH batteries are cheaper upfront, Li-ion batteries provide better long-term value due to their longer lifespan and efficiency.
🔋 Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery: Higher Initial Cost, Better Long-Term Savings
🚫 More expensive upfront – Li-ion batteries cost more initially due to advanced technology, higher energy density, and superior lifespan.
✅ Cost-effective over time – Thanks to their longer cycle life (500-1,500 cycles) and lower replacement frequency, Li-ion batteries reduce long-term costs.
✅ Best for long-term applications – Ideal for electric cars, solar energy storage, and high-performance industrial devices, where battery longevity matters.
🔋 Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery: Lower Initial Cost, More Frequent Replacements
✅ Cheaper upfront – NiMH batteries are a more budget-friendly option for short-term or low-power applications.
🚫 Higher maintenance cost – Due to shorter lifespan (300-500 cycles) and higher self-discharge rate, NiMH batteries require more frequent replacements, leading to higher total cost over time.
✅ Good for budget-conscious consumers – NiMH batteries are still a viable choice for household rechargeable batteries, cordless phones, and non-intensive electronics.
🏆 Conclusion: Which Battery is More Cost-Effective?
Although NiMH batteries have a lower initial cost, Lithium-ion batteries offer better long-term value. Their longer cycle life, better energy efficiency, and fewer replacements make them the cost-effective choice for high-performance applications like electric vehicles, medical devices, and renewable energy systems.
🔗 Want to Learn More? Read This Detailed Comparison:
For a comprehensive breakdown of Lithium vs NiMH battery performance, lifespan, cost, and applications, check out our full guide:
👉 Lithium vs NiMH Battery Packs: A Detailed Comparison
6. Environmental Impact: Which Battery is More Eco-Friendly?
As concerns about e-waste, resource depletion, and sustainability grow, choosing an eco-friendly battery is crucial. Both Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries have environmental impacts, but they differ in toxic material content, recyclability, and resource extraction processes.
🌱 Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery: Fewer Toxins, But Mining Impact
✅ Lower toxic substance content – Li-ion batteries contain fewer hazardous materials compared to older battery types like lead-acid or NiMH.
🚫 Environmental impact of lithium & cobalt mining – Extracting lithium, cobalt, and rare metals for Li-ion batteries can cause habitat destruction, water depletion, and pollution.
✅ Recycling is improving – While Li-ion battery recycling is still developing, advancements in closed-loop recycling and second-life battery applications are making disposal more sustainable.
🌍 Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery: Easier to Recycle, But Nickel Mining Concerns
✅ More recyclable – NiMH batteries are easier to recycle than Li-ion, with established recycling programs handling nickel recovery efficiently.
🚫 Nickel mining impact – The extraction and processing of nickel contribute to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and soil contamination.
✅ Lower risk of hazardous leakage – NiMH batteries have fewer volatile chemicals, reducing environmental risks in case of improper disposal.
🏆 Conclusion: Which Battery is Greener?
Neither battery is completely environmentally friendly, but Lithium-ion batteries have a lower toxic footprint if recycling technology continues to advance. NiMH batteries are easier to recycle, but nickel mining has significant environmental drawbacks. For sustainable energy storage, choosing rechargeable batteries with long lifespans and proper recycling programs is essential.
7. Applications: Which Battery is Best for Your Needs?
The choice between Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries depends on energy requirements, weight considerations, and long-term performance. Each battery type has specific use cases where it performs best.
🔋 Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery: Best for High-Power, Long-Lasting Applications
✅ Ideal for high-performance electronics – Used in smartphones, laptops, drones, and electric vehicles (EVs) due to high energy density and efficiency.
✅ Perfect for portable & lightweight devices – Preferred for applications requiring compact design and longer battery life, such as wearable devices, medical equipment, and aerospace technology.
✅ Reliable for energy storage solutions – Frequently used in solar battery storage, grid energy backup, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
🔋 Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery: Best for Low-Power, Budget-Friendly Devices
✅ Common in household electronics – Found in TV remotes, cordless phones, digital cameras, and gaming controllers, where energy demands are lower.
✅ Used in hybrid vehicles – Hybrid cars like the Toyota Prius use NiMH battery packs due to cost-effectiveness and proven reliability.
🚫 Not ideal for high-energy applications – Due to lower energy density, NiMH batteries are less suitable for power-hungry devices like EVs and industrial power tools.
🏆 Conclusion: Which Battery Should You Choose?
- Choose Li-ion if you need a high-power, long-lasting battery for smartphones, laptops, electric cars, and professional tools.
- Choose NiMH for household electronics, hybrid vehicles, and budget-friendly rechargeable solutions where high energy density isn’t required.
🔗 Want More Insights? Read the Full Battery Comparison Here:
Which Battery is Better for Performance: NiMH or Lithium?
When choosing between Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries, performance is a key factor. The right battery depends on your energy demands, lifespan expectations, and application requirements.
🔋 Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery: Superior Performance & Efficiency
✅ Higher energy density – Li-ion batteries store more power per unit of weight (~250 Wh/kg vs. 60-120 Wh/kg for NiMH), making them lighter and more efficient.
✅ Longer cycle life – With 500-1,500 charge cycles, Li-ion batteries last significantly longer than NiMH (~300-500 cycles).
✅ Better charge retention – Low self-discharge rate (5-10% per month) means they hold a charge much longer than NiMH (20-30% per month).
✅ Ideal for high-performance applications – Used in smartphones, laptops, drones, power tools, and electric vehicles (EVs) where power efficiency and longevity matter.
🔋 Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery: Budget-Friendly but Less Efficient
✅ Lower initial cost – NiMH batteries are cheaper upfront, making them a good choice for budget-conscious applications.
🚫 Lower energy density – Bulkier and heavier compared to Li-ion, making them less suitable for portable devices.
🚫 Shorter lifespan & faster self-discharge – NiMH batteries degrade faster and need more frequent replacements.
✅ Good for low-power devices – Commonly used in remote controls, digital cameras, power tools, and some hybrid vehicles (e.g., Toyota Prius).
🏆 Conclusion: Which Battery is Best for Performance?
While NiMH batteries remain a cost-effective solution for low-power applications, Lithium-ion batteries are the superior choice for most modern, high-performance devices. Their higher energy efficiency, longer lifespan, and better charge retention make them ideal for smartphones, laptops, EVs, and professional tools.
🔗 Want to Learn More? Read This Detailed Comparison:
👉 Comparing Li-ion vs NiMH Batteries: Which is the Better Choice?
Battery Lifespan: Which One Lasts Longer?
Battery lifespan plays a crucial role in cost-effectiveness, performance, and long-term reliability, especially for devices that require frequent charging such as smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles (EVs), and power tools.
🔋 Lithium-ion (Li-ion) Battery: Longer Lifespan & Better Durability
✅ Higher cycle life – Li-ion batteries typically last between 500 to 1,500 charge cycles, with premium variants (such as Tesla EV batteries and advanced energy storage systems) exceeding 2,000 cycles under optimal conditions.
✅ Better for frequent charging – Li-ion batteries are designed to withstand daily charge-discharge cycles with minimal capacity loss, making them ideal for high-drain devices.
✅ Slower capacity degradation – Equipped with Battery Management Systems (BMS), Li-ion batteries experience less performance loss over time, ensuring higher efficiency and stability.
🔋 Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Battery: Shorter Lifespan, More Frequent Replacements
🚫 Lower cycle life – NiMH batteries typically last 300 to 500 cycles, meaning they require more frequent replacements compared to Li-ion batteries.
🚫 Faster capacity degradation – NiMH batteries experience greater energy loss over time, especially under high discharge rates or fluctuating temperature conditions.
✅ Still useful for low-power applications – Despite their shorter lifespan, NiMH batteries are commonly used in household electronics, hybrid vehicles (e.g., Toyota Prius), and rechargeable AA/AAA batteries.
🏆 Conclusion: Which Battery Lasts Longer?
For long-lasting performance, fewer replacements, and better overall efficiency, Lithium-ion batteries are the superior choice. Their higher cycle life, slower degradation, and energy retention make them ideal for electric vehicles, high-performance consumer electronics, and industrial applications.
What is a Disadvantage of Using NiMH Batteries?
While Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries are a cost-effective and widely used rechargeable battery option, they have several drawbacks compared to Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. These limitations impact battery efficiency, longevity, and performance in various applications.
🚫 1. High Self-Discharge Rate: Loses Charge Quickly
🔴 NiMH batteries can lose up to 30% of their charge per month, even when not in use.
🔴 In comparison, Li-ion batteries only lose about 5-10% per month, making them better for standby or backup power applications.
🔴 This makes NiMH batteries less reliable for devices that sit idle for long periods, such as emergency flashlights, backup power supplies, and seasonal electronics.
🚫 2. Memory Effect: Reduced Capacity Over Time
🔴 Frequent partial charging can cause the “memory effect”, where the battery remembers a smaller charge capacity, leading to reduced energy storage.
🔴 This issue is less common in Li-ion batteries, which do not suffer from memory effects and maintain consistent performance over time.
🔴 To prevent capacity loss, NiMH batteries require full discharge cycles, which can be inconvenient for users.
🚫 3. Overcharging Sensitivity: Risk of Performance Degradation
🔴 Overcharging NiMH batteries can cause crystal formation on the electrodes, reducing their ability to hold a charge.
🔴 This can lead to shortened lifespan and reduced efficiency, making NiMH batteries less suitable for high-power, frequently charged devices.
🔴 Advanced charging systems are often needed to prevent overcharging, increasing maintenance complexity.
🏆 Conclusion: Why NiMH Batteries Have Limitations
While NiMH batteries remain a viable option for low-power applications such as household electronics, digital cameras, and some hybrid vehicles, they come with major drawbacks like high self-discharge rates, memory effect, and sensitivity to overcharging.
For better performance, longer lifespan, and improved energy efficiency, Lithium-ion batteries are the preferred choice for smartphones, laptops, electric vehicles, and high-performance electronics.
What is the Biggest Disadvantage of a Lithium-Ion Battery?
While Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the preferred choice for high-performance electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and energy storage, they come with certain drawbacks that impact cost, safety, and environmental sustainability.
🚫 1. High Cost Due to Rare Metals
🔴 Li-ion batteries require expensive materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, making them costlier to produce than NiMH or lead-acid batteries.
🔴 The demand for EVs, consumer electronics, and renewable energy storage has driven up lithium and cobalt prices, further increasing manufacturing costs.
🔴 NiMH batteries are often cheaper, making them more attractive for budget-conscious applications.
🚫 2. Environmental Concerns: Mining & Recycling Challenges
🔴 Lithium and cobalt extraction contribute to environmental damage, water depletion, and ethical mining concerns.
🔴 Li-ion batteries are harder to recycle than NiMH, requiring specialized recycling facilities to prevent toxic waste and battery fires.
🔴 Sustainability concerns have led to research into alternatives, such as solid-state and sodium-ion batteries.
🚫 3. Temperature Sensitivity & Safety Risks
🔴 Li-ion batteries are highly sensitive to extreme temperatures, which can affect performance, efficiency, and lifespan.
🔴 Excessive heat (>45°C / 113°F) can cause faster degradation, while cold temperatures (<0°C / 32°F) reduce charge capacity.
🔴 Thermal runaway risk – In rare cases, overheating or physical damage can lead to battery swelling, fires, or explosions, requiring strict battery management systems (BMS).
🚫 4. Repairability & Replacement Complexity
🔴 Li-ion battery packs are often sealed units, making repairs difficult and costly.
🔴 Unlike NiMH batteries, which can be easily replaced in hybrid vehicles or household devices, many Li-ion battery-powered devices (e.g., smartphones, EVs, laptops) require specialized replacement procedures.
🔴 Battery recycling infrastructure is still developing, making disposal and reuse efforts more complex.
🏆 Conclusion: Are Li-ion Batteries Worth It Despite Their Drawbacks?
Despite these disadvantages, Lithium-ion batteries remain the best choice for applications requiring high energy density, long lifespan, and superior performance.
However, for cost-sensitive, easily replaceable, or lower-power applications, NiMH batteries might be a more affordable and practical alternative.
FAQs
✅ Not recommended unless the device supports it.
Why?
- Voltage differences – NiMH: 1.2V per cell, Li-ion: 3.6V per cell (using Li-ion may damage circuits).
- Charging incompatibility – NiMH and Li-ion require different chargers.
- Battery Management System (BMS) – Li-ion batteries need voltage regulation, which NiMH devices usually lack.
When is it possible?
✔ If the device explicitly supports both NiMH & Li-ion.
✔ If using a compatible Li-ion battery pack with matching voltage.
✔ If modifying the device (not recommended for non-experts).
📌 Conclusion: Always check the device manual before switching to Li-ion, as improper replacement can cause malfunctions.
✅ Yes, NiMH batteries are generally safer.
Why?
- Lower fire risk – NiMH batteries do not experience thermal runaway, reducing the risk of overheating or explosion.
- No volatile chemicals – Unlike Li-ion, NiMH batteries lack flammable electrolytes, making them more stable.
What about Li-ion?
✔ Safe when used properly – Most Li-ion batteries have built-in safety features like Battery Management Systems (BMS).
✔ More sensitive to damage – Overcharging, puncturing, or exposure to extreme heat can lead to failure.
📌 Conclusion: While NiMH batteries are inherently safer, Li-ion batteries are safe when used according to manufacturer guidelines and with proper protection systems.
✅ Higher energy density, longer lifespan, and better efficiency.
Key Reasons:
- Higher energy density – Li-ion batteries store more energy per kg, allowing EVs to travel longer distances per charge.
- Longer lifespan – Li-ion batteries last 1,000+ charge cycles, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Lightweight & compact – Li-ion packs are smaller and lighter, improving EV efficiency and range.
- Better power output – Delivers higher power for acceleration and supports fast charging technology.
📌 Conclusion: EVs use Lithium-ion batteries because they offer superior performance, efficiency, and durability, making them ideal for modern electric transportation.
✅ Avoid extreme temperatures, overcharging, and deep discharges.
Best Practices for Longer Battery Life:
- Keep charge between 20-80% – Avoid fully charging (100%) or deep discharging (0%) to reduce wear.
- Avoid extreme temperatures – High heat (>45°C/113°F) degrades battery life, and cold (<0°C/32°F) reduces efficiency.
- Use the right charger – Always use a manufacturer-approved charger to prevent overvoltage and overheating.
- Unplug when fully charged – Prolonged charging can cause unnecessary stress on the battery.
- Store properly – If not in use for long periods, store at 40-50% charge in a cool, dry place.
📌 Conclusion: Following these simple steps maximizes battery lifespan, ensuring better performance and longevity for your smartphone, laptop, or EV battery.
Limited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
 Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide
Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide No hidden fees – transparent pricing
No hidden fees – transparent pricing Guaranteed quality with on-time deliver
Guaranteed quality with on-time deliverConclusion: Which Battery Should You Choose?
Choosing between Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries depends on your performance requirements, budget, and application needs. Each battery type has its advantages, making them suitable for different use cases.
🔋 Choose Lithium-ion (Li-ion) If You Need:
✅ High energy density – Best for smartphones, laptops, power tools, and electric vehicles (EVs) where compact size and long battery life matter.
✅ Longer cycle life – Lasts 500-1,500 charge cycles, making it a better long-term investment.
✅ Lower self-discharge – Retains charge longer, ideal for backup power systems, medical devices, and seasonal-use electronics.
🔋 Choose Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) If You Need:
✅ Lower upfront cost – Ideal for budget-conscious applications where high performance isn’t required.
✅ Good for low-power devices – Works well in remote controls, cordless phones, hybrid vehicles, and household rechargeable batteries.
✅ Easier recycling – NiMH batteries have a more developed recycling infrastructure compared to Li-ion.
🏆 Final Verdict: Li-ion Wins for Performance, NiMH for Affordability
If you need high power output, long cycle life, and compact size, Lithium-ion is the clear winner. However, for low-power applications where cost is a bigger concern, NiMH remains a practical and cost-effective choice.
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




