Quick Leads
In modern electronic devices, the printed circuit board (PCB) plays a vital role in ensuring the efficient flow of electricity between components. For engineers, technicians, and designers, a solid understanding of PCB components is essential for circuit board design, troubleshooting, and repair.
This article provides a detailed breakdown of key PCB components, their functions, and practical tips on how to identify and use them effectively.
Essential PCB Components and Their Functions
A circuit board (PCB) consists of several critical components, including:
- Resistors – Control current flow and voltage distribution
- Capacitors – Store and release electrical energy
- Inductors – Filter signals and manage electromagnetic interference
- Diodes – Direct electrical flow in one direction
- Transistors – Act as switches or signal amplifiers
- Integrated Circuits (ICs) – Perform complex processing functions
- Connectors – Provide interfaces for external devices
Each of these PCB components plays a crucial role in regulating and directing electrical signals, ensuring that the circuit functions efficiently.
How to Identify PCB Components in Your Design & Repairs
Now that we’ve covered the basic components, let’s dive deeper into how to identify PCB parts in your electronic designs and repairs.
Want to explore Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) PCBs? Learn how custom PCB assembly enhances performance and reliability for various applications. 👉 [Read More About SMT PCB Design]
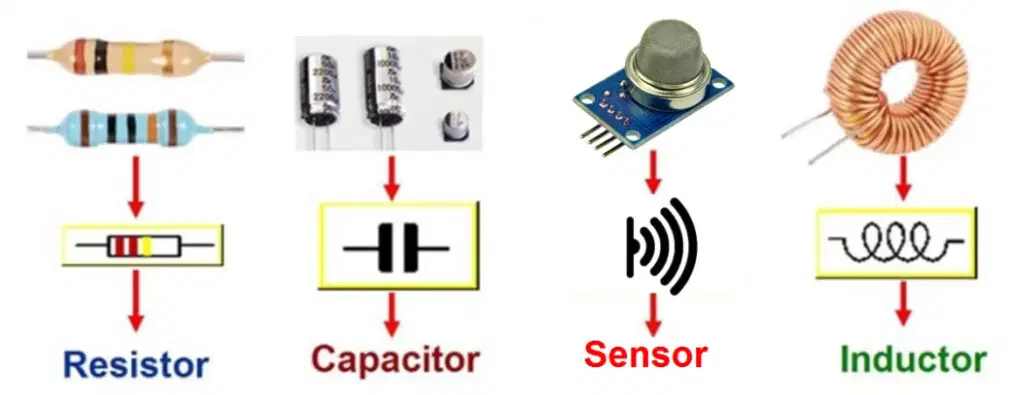
Key Components of a Circuit Board: Passive vs. Active PCB Parts Explained
A printed circuit board (PCB) is made up of various components that work together to ensure electronic devices operate efficiently. These PCB components can be categorized into two main types:
Passive Components – These do not require external power to function. They include:
- Resistors – Control current flow and voltage levels
- Capacitors – Store and release electrical energy
- Inductors – Filter signals and manage electromagnetic interference
Active Components – These require an external power source to function. Examples include:
- Transistors – Act as amplifiers or switches
- Integrated Circuits (ICs) – Process signals and control circuit operations
- Diodes – Allow current to flow in only one direction
Understanding the difference between active and passive components is crucial for PCB design, troubleshooting, and repair.
1. Resistors
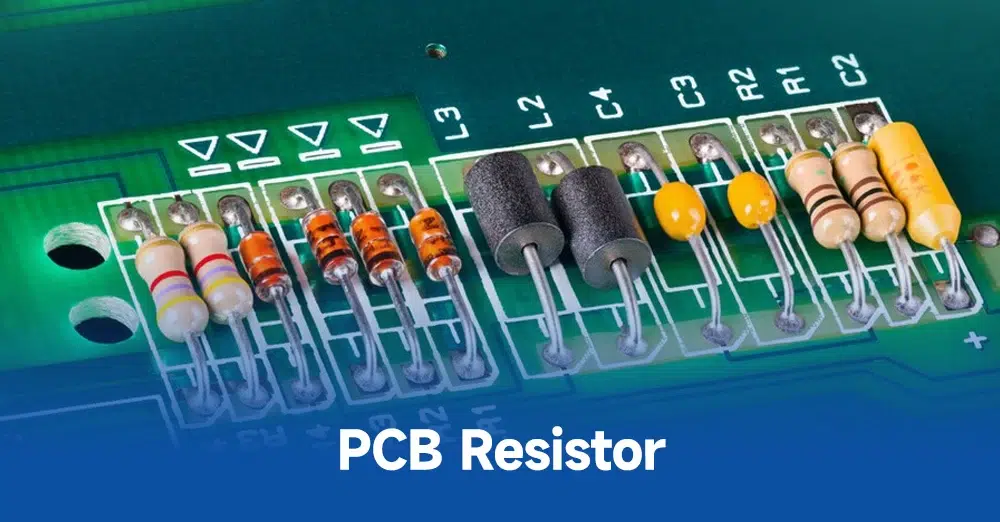

Resistors are fundamental components on a PCB. Their primary function is to limit the flow of electrical current, protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes. Resistors come in various values, typically marked in a numerical code (e.g., “104” for 100,000 ohms). In advanced designs, resistors also play a role in voltage division, helping distribute voltage correctly across the circuit.
2. Capacitors
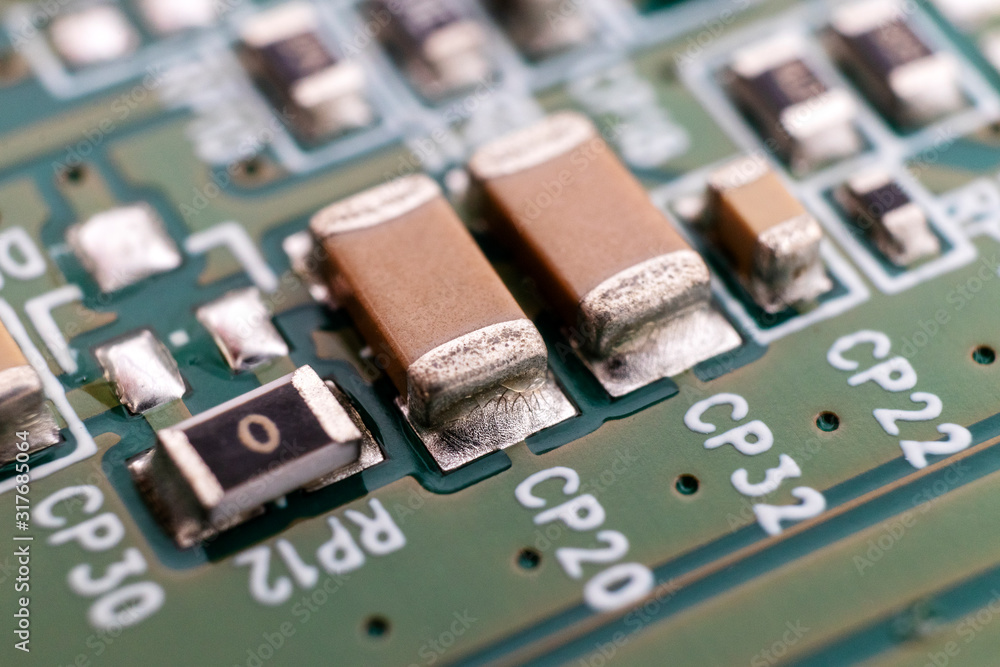
Capacitors store electrical energy and release it when required, ensuring a stable power supply. They are essential for filtering noise, smoothing voltage fluctuations, and stabilizing circuits that rely on precise timing (e.g., oscillators). Common types include ceramic capacitors and electrolytic capacitors, each serving different capacitance needs.
3. Inductors
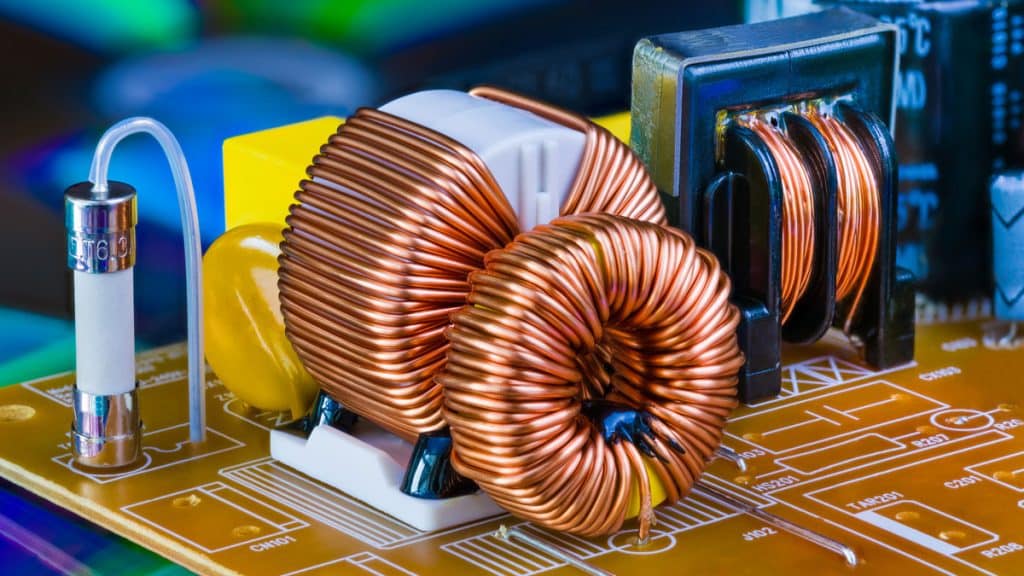
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field and are vital for filtering or energy storage. They help smooth power supply fluctuations and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). Inductors are commonly used in power supply circuits, making them critical for maintaining stability in high-frequency applications.
4. Diodes
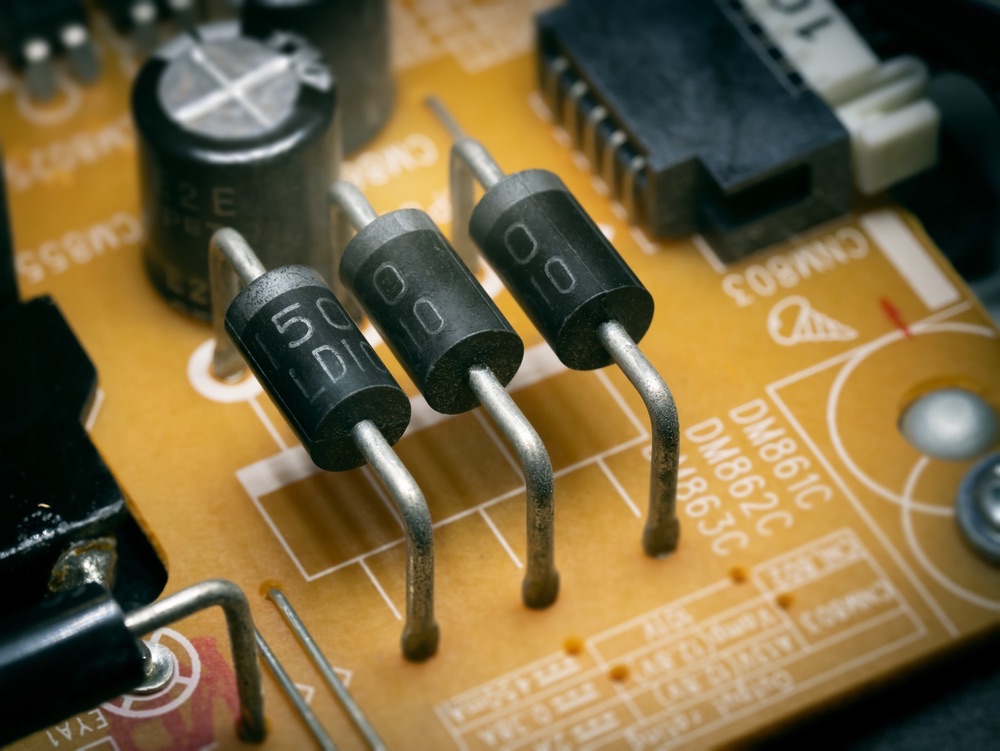
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field and are vital for filtering or energy storage. They help smooth power supply fluctuations and reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI). Inductors are commonly used in power supply circuits, making them critical for maintaining stability in high-frequency applications.
5. Transistors
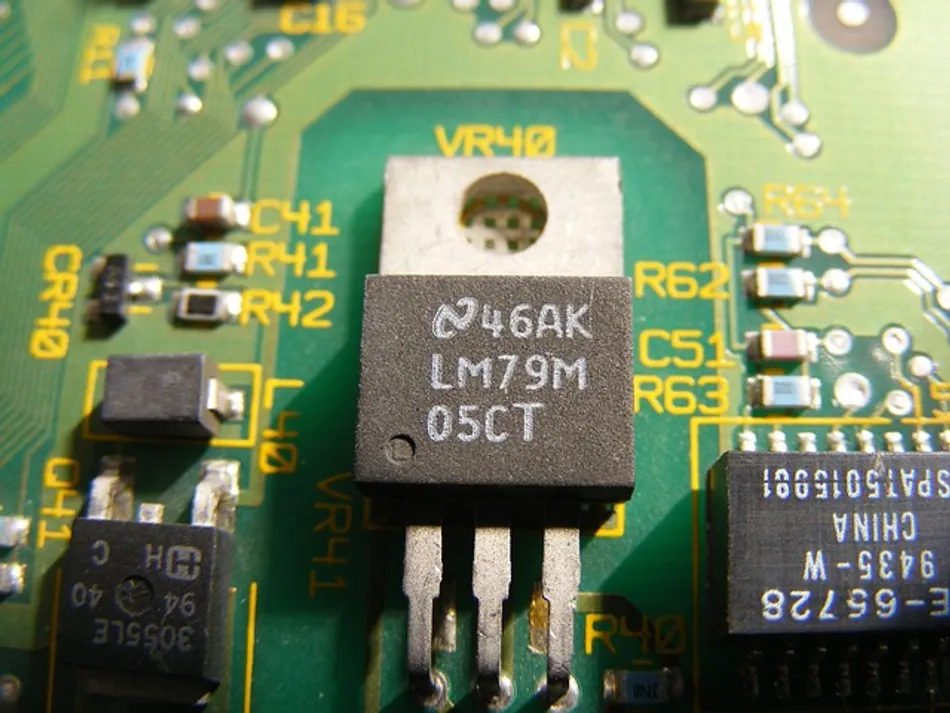

Transistors act as amplifiers or switches, controlling the flow of electrical current between terminals. They are used in digital logic circuits, signal amplification, and switching applications. Transistors come in types like bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs), each suitable for different uses.
6.Transformers
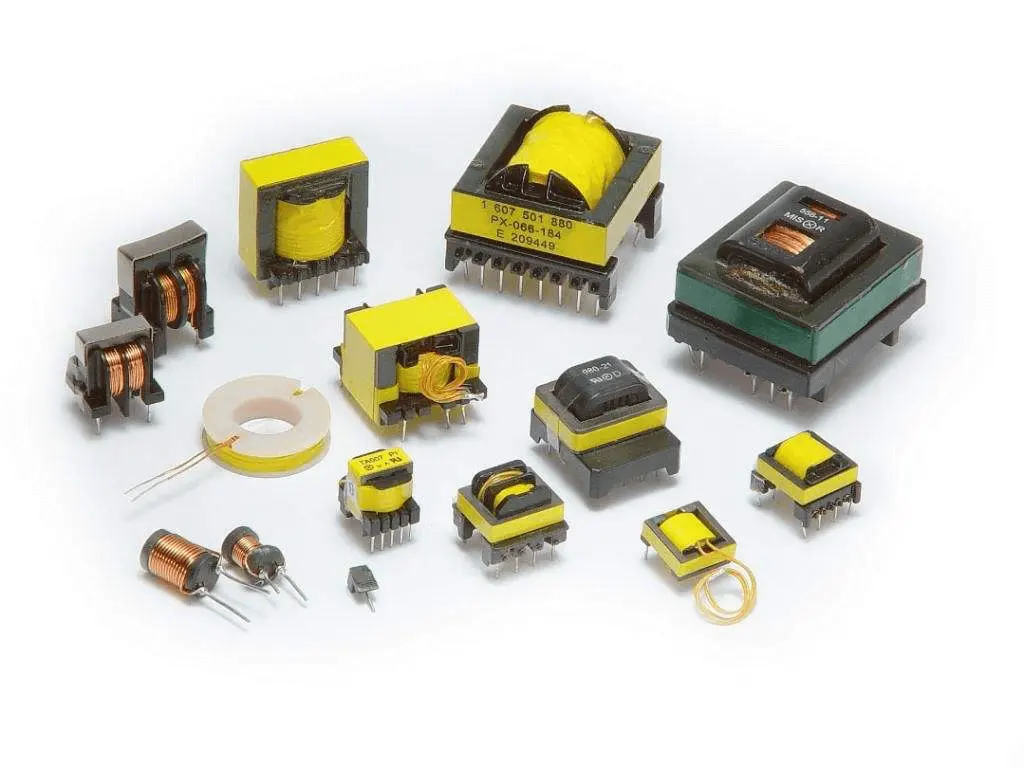

Transformers are electrical devices used to change the voltage level in alternating current (AC) circuits. They are essential for regulating the voltage to suitable levels for various components and devices. A transformer works by transferring electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. In a PCB, transformers are typically used to step up or step down voltage, isolate sections of a circuit, or filter unwanted frequencies. They come in various shapes and sizes depending on the application and power requirements. Transformers are commonly found in power supplies, audio equipment, and communication systems.
7. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
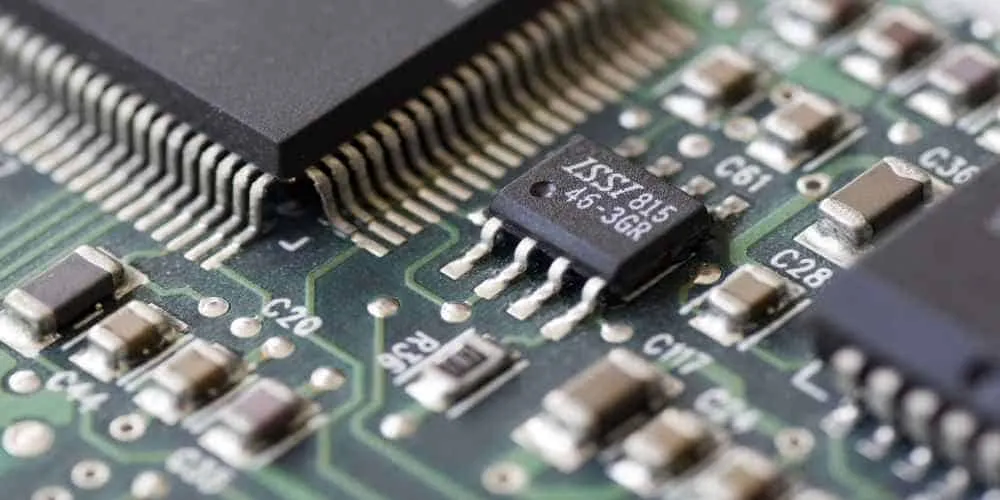
ICs combine multiple components (such as transistors, capacitors, and resistors) into a single package, performing complex functions such as signal processing and power management. ICs are essential for reducing size while enhancing performance in devices like smartphones, computers, and audio equipment.
8.Crystal Oscillators

Oscillators generate periodic waveforms that are crucial for timing and signal generation. These waveforms help synchronize components in systems like clocks, microcontrollers, and timers. Oscillators are widely used in communication systems and signal processing.
9.Switches and Relays
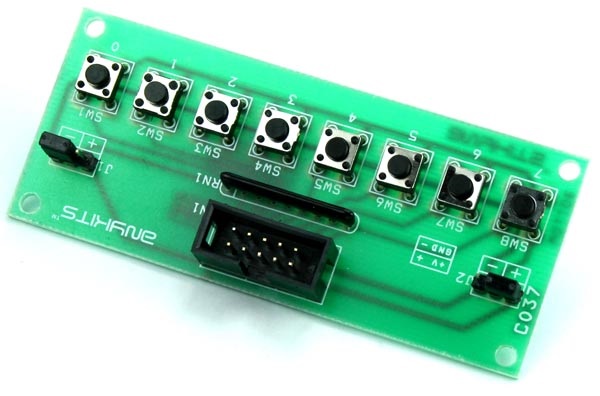
Switches control the flow of electricity by opening or closing a circuit. There are many types of switches, including toggle switches, push-button switches, and slide switches. Switches are commonly used to turn devices on and off, as well as to control specific functions within a circuit.
10. Potentiometers

Potentiometers are adjustable resistors that control the resistance in a circuit. They are used in applications such as volume controls, brightness adjustments, and tuning circuits. Potentiometers allow for variable control of voltage or current, making them versatile components in many electronic systems.
11. Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs)
SCRs are semiconductor devices used for controlling large currents and voltages. These components are particularly useful in power regulation systems, where they can switch large currents on and off with precision. SCRs are commonly found in industrial systems, such as motor control circuits.
12. Sensors
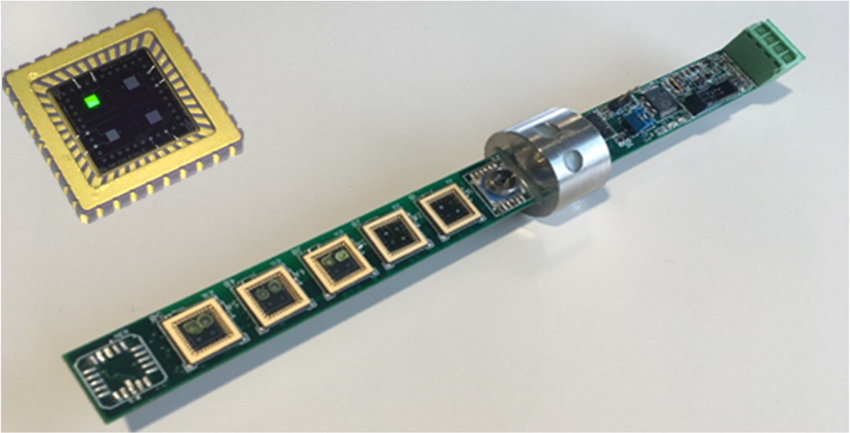
Sensors are devices that monitor environmental conditions such as temperature, pressure, and humidity. They convert these changes into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the circuit. Sensors are essential in systems like IoT, automotive electronics, and healthcare devices, making them key components in modern technology.
How to Identify SMD Components on a Circuit Board?
Surface-mount devices (SMDs) are small components soldered directly to the surface of a PCB. These components are typically flat, rectangular, or square in shape. They are identified by:
-
Numerical codes (e.g., “104” for resistors).
-
Package types: Common types include SOIC (Small Outline Integrated Circuit) for ICs.
What Are the Round Things on a Circuit Board?
The round components on a PCB are usually pads and vias:
-
Pads: Larger circles of exposed copper used to attach components with leads.
-
Vias: Small circular holes that connect different layers in a multi-layer PCB design.
What Are the Four Main Parts of a Basic Circuit?
A basic circuit typically includes:
-
Battery: Provides electrical power.
-
Wires: Conduct electricity between components.
-
Switch: Controls the circuit, turning it on or off.
-
Load: A component (e.g., light bulb or motor) that consumes electrical energy.
What Are the Lines on a Circuit Board Called?
The lines on a circuit board are called traces. These copper pathways guide the electrical current to various components, forming the electrical network that connects the circuit’s parts.
What Are the Black Cylinders on a Circuit Board?
The black cylinders are likely inductors, which store energy in a magnetic field. They are used for filtering, tuning, and suppressing electrical noise in circuits.
How to Identify Components on a Circuit Board?
Identifying components on a PCB involves recognizing designators like:
-
R for resistors.
-
C for capacitors.
-
Q for transistors. Components often have numerical codes or symbols that indicate their specific values and functions.
How Do Capacitors, Resistors, and Transistors Work on a Circuit Board?
-
Resistors: Limit current flow to protect sensitive components.
-
Capacitors: Store and release energy, smoothing out voltage fluctuations.
-
Transistors: Amplify signals or switch current on and off.
What Are the Functions of Integrated Circuits in a PCB?
ICs combine multiple transistors and other components into a single package, enabling complex functions like signal processing, computation, and power management. They are essential for reducing size while improving performance.
What Is the Role of Sensors on a Circuit Board?
Sensors detect environmental changes (e.g., temperature, pressure) and convert these into electrical signals that the circuit processes. They are crucial in systems such as IoT, automotive electronics, and health monitoring.
What Are Potentiometers and Switches on a Circuit Board?
-
Potentiometers: Adjustable resistors used for controlling voltage, like in volume controls.
-
Switches: Devices that control the flow of electricity by opening or closing the circuit.
What Is the SCR (Silicon-Controlled Rectifier) on a Circuit Board?
SCRs are used for controlling large currents in power regulation systems, especially in industrial circuits where high precision is required.
Limited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
 Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide
Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide No hidden fees – transparent pricing
No hidden fees – transparent pricing Guaranteed quality with on-time deliver
Guaranteed quality with on-time deliverConclusion
In conclusion, a circuit board is more than just a physical platform; it’s an intricate network of components working in tandem. By understanding how to identify and utilize resistors, capacitors, transistors, and other parts, you’ll be equipped to design, repair, and optimize electronic devices effectively.
At Unit Circuits, we provide a comprehensive range of services to support your electronics project, from PCB manufacturing to full turnkey solutions, including parts sourcing and assembly. Whether you’re in the early stages of prototyping or looking to scale up to mass production, we ensure a seamless process with efficient and high-quality results.
We also provide functional testing for free with every PCBA order, allowing you to validate your designs early. Our prototyping services are ideal for business users, and we also offer additional support for specific designs, such as those involving embedded systems or complex electronics integration.
At Unit Circuits, we’re dedicated to minimizing setbacks and maximizing yield, ensuring a smooth and efficient experience for all developers and makers, whether you’re working on your first project or scaling to a larger production run.
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




