Quick Leads
💡 Full-service PCB Assembly?
We offer turnkey solutions from PCB manufacturing to testing.
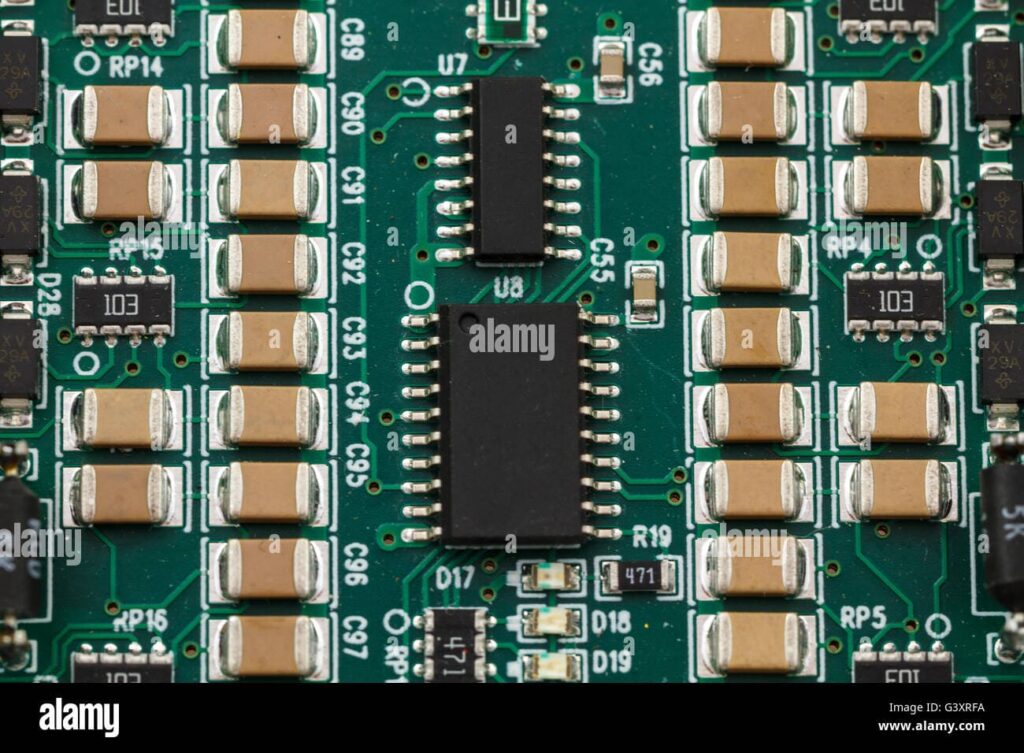
What Are PCB Component Codes?
PCB components are the individual parts that make up a printed circuit board. From resistors and capacitors to transistors and ICs, these electronic circuit board components are essential for powering devices. Below is a PCB components list that outlines the most common parts:
- Resistors: Control current flow.
- Capacitors: Store and release electrical charge.
- ICs (Integrated Circuits): Perform processing tasks.
By understanding what PCB components are, you can better design and troubleshoot your circuit boards.
Common PCB Component Codes
A PCB parts list is essential for identifying and assembling components. This list typically includes component names, PCB component codes, and their functions.
Component | Code | Function |
Resistor | R | Limits current flow |
Capacitor | C | Stores and releases electrical energy |
Inductor | L | Opposes changes in current flow |
Integrated Circuit | U | Performs complex functions like data processing |
Diode | D | Allows current flow in one direction |
Transformer | T | Transfers electrical energy between circuits |
Test Point | TP | Used for testing signals and diagnosing issues |
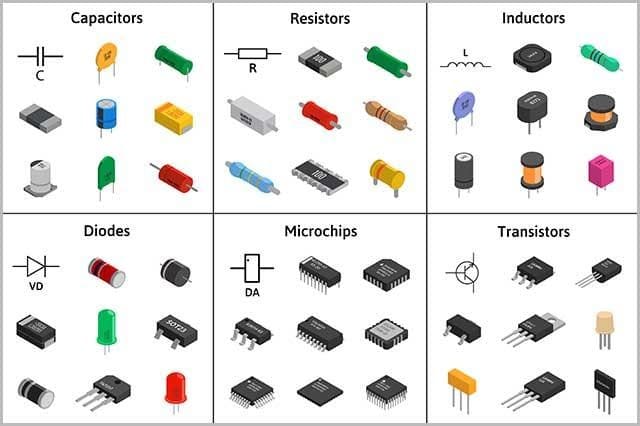
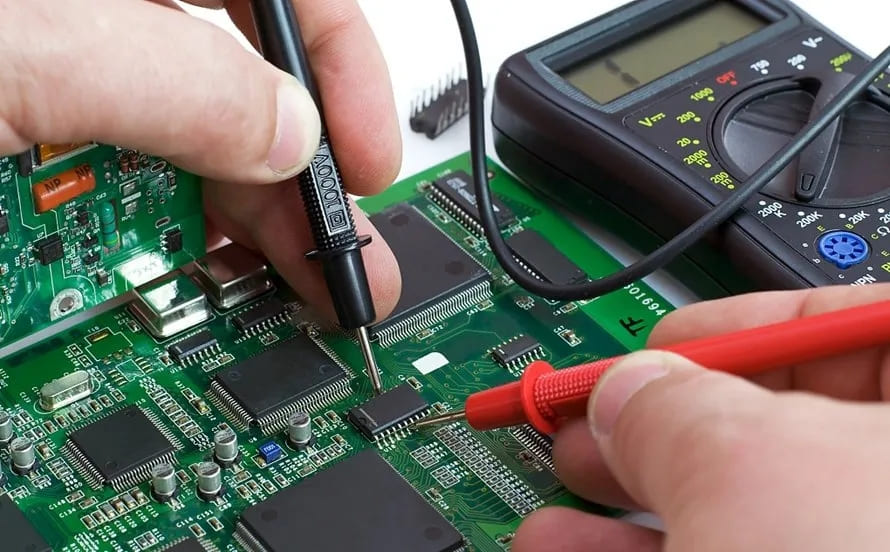
How Do Professionals Identify Parts on a PCB?
1. Printed Labels
-
Most circuit boards have little letters next to the parts that tell you what kind of part it is. For example, “R” for resistors, “C” for capacitors, and “L” for inductors.
2. Symbols
-
Sometimes, instead of using letters, circuit symbols are used to show what kind of part it is. For example, diodes are often marked with a small arrow to show which way the current goes.
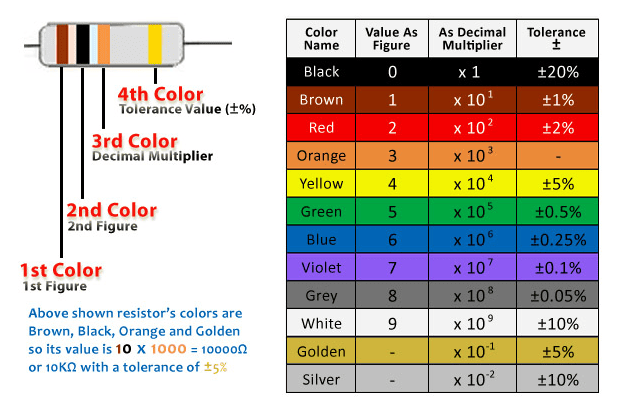
3. Color Codes
-
Resistors have little colored bands on them that tell you what their resistance is. This system is used all over the world, and everybody uses the same colors, so you can tell what the resistance is just by looking at the colors.
Understanding the Function of Key PCB Components
Understanding the functions of common PCB components is key to creating effective circuit designs. Below is an overview of circuit board components and what they do:
- Basic Components of a Circuit Board: These include resistors, capacitors, and diodes.
- Embedded PCB Components: Found inside multilayer PCBs for advanced functionality.
- Through-Hole Components: Provide durability and are ideal for mechanical stress.
Each of these PCB components and their functions plays a critical role in ensuring proper circuit operation.
1. Passive Components
- Resistors (R): Resistors limit the flow of current. They ensure that parts that can’t handle a lot of current don’t get too much.
- Capacitors (C): Capacitors store and release electricity. They’re used to stabilize voltage changes and filter noise.
- Inductors (L): Inductors oppose current changes, store energy, and filter noise from power supplies.
2. Active Components
- Diodes (D): Diodes only allow current to flow in one direction, protecting components from damage caused by reverse current.
- Transistors (Q): Transistors amplify electrical signals or act as switches in circuits.
- Integrated Circuits (U): ICs are complex components containing multiple functions like data processing, signal amplification, or logic control.
How to Solder Components to a PCB
Soldering is a vital step in PCB components assembly. Here’s how to solder components to a PCB:
- Prepare the PCB and Components: Gather the circuit board and all PCB components.
- Identify PCB Component Codes: Use the PCB parts list for quick identification.
- Solder Components: Begin with small components like resistors and capacitors.
By following this guide, you can achieve precise PCB manufacturing with components, ensuring high-quality results.
Common PCB Standards and Coding Systems
1. IPC-7351: Land Pattern Design
-
It ensures that components are placed correctly for proper soldering and performance.
2. IEC 61360: Component Identification
-
Following this ensures that all manufacturers and designers “speak the same language” when referencing parts.

Troubleshooting PCB Components: What the Codes Tell Us
1. Identifying Faulty Components
- Reference designators (e.g., R3, C5) allow professionals to pinpoint problematic parts quickly.
2. Verifying Design Integrity
- During design or assembly, codes help engineers confirm each component is in the right place.
3. Optimizing Repairs
- By using standardized codes, replacement parts can be ordered and installed efficiently.
Case Study: A faulty diode (D3) was identified in a motor controller PCB. Using its component code, the technician quickly replaced it, restoring functionality in under an hour.
Frequently Asked Questions
- R for resistors
- C for capacitors
- L for inductors
- U for integrated circuits (ICs)
- D for diodes
- T for transformers
- TP for test points
Components are identified using printed labels (e.g., “R” for resistors), color codes (e.g., resistor bands), and circuit symbols. Reference designators like R1 or C3 further specify the exact component on the board.
IPC-7351 ensures proper pad design for components, while IEC 61360 standardizes component names for clear communication. Following these standards improves reliability and reduces manufacturing errors.
Professionals use tools like multimeters and reference designators (e.g., R5, C8) to locate and test faulty components. This method ensures accurate repairs and minimal downtime.
Limited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
 Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide
Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide No hidden fees – transparent pricing
No hidden fees – transparent pricing Guaranteed quality with on-time deliver
Guaranteed quality with on-time deliverSummary
Next Steps
🔧 Want to avoid these manufacturing issues with a trusted partner?
👉 See how our Turnkey PCB Assembly can help »
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




