Quick Leads
SMT vs. THT: Which PCB Manufacturing Technology is Right for Your Needs?
Introduction
💡 Full-service PCB Assembly?
We offer turnkey solutions from PCB manufacturing to testing.
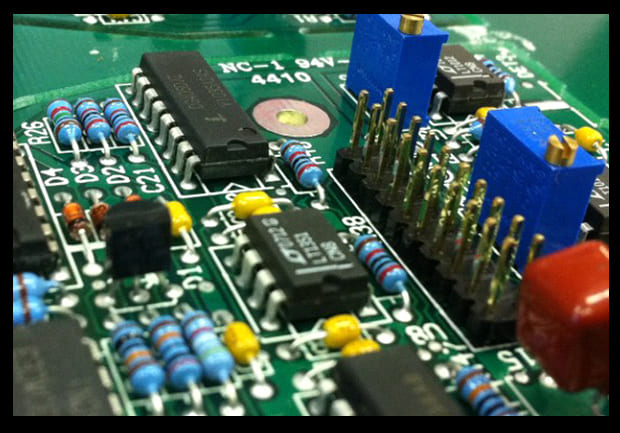
Quick Overview: SMT vs. THT Comparison Table
|
Feature |
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) |
Through-Hole Technology (THT) |
|
Assembly Process |
Automated, high-speed |
Manual or semi-automated |
|
Cost Efficiency |
Cost-effective for high-volume production |
Higher cost due to manual labor |
|
Mechanical Strength |
Less durable under stress |
Ideal for high-stress environments |
|
Applications |
Consumer electronics, IoT devices |
Aerospace, industrial equipment |
|
Repairability |
Complex, requires special tools |
Easier to access and repair |
|
Thermal Performance |
Requires advanced heat management |
Superior heat dissipation |
Key Differences Between SMT and THT
1. Assembly Process
-
SMT: Components are mounted directly onto the PCB surface using automated pick-and-place machines, ideal for high-speed, high-volume production.
-
THT: Components are inserted through pre-drilled holes in the PCB and soldered, offering better mechanical strength.
2. Component Size and Density
-
SMT: Enables smaller components and double-sided PCB designs, perfect for compact, lightweight devices like IoT gadgets.
-
THT: Uses larger components, suitable for low-density layouts or high-power applications.
3. Mechanical Strength
-
THT excels in environments with vibration or mechanical stress, such as aerospace and automotive industries.
-
SMT connections, while efficient, are less durable under stress.
4. Cost Efficiency
-
SMT: Cost-effective for mass production due to its automated process.
-
THT: Higher labor costs make it more suitable for low-volume or specialized projects.
5. Thermal Performance
-
THT: Superior heat dissipation through the PCB, ideal for high-power devices.
-
SMT: Requires advanced techniques like heat sinks or thermal vias to manage heat.
Real-World Applications of SMT and THT
SMT Applications
-
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, tablets, and wearables benefit from SMT’s compact design capabilities.
-
IoT Devices: High-speed, space-efficient designs make SMT a top choice for smart home devices.
-
Automotive Electronics: Used in lightweight systems like ADAS and infotainment.
THT Applications
-
Aerospace & Defense: Reliable under extreme conditions, ideal for mission-critical systems.
-
Industrial Equipment: Handles vibration and stress in heavy machinery and robotics.
-
Medical Devices: Preferred for high-reliability applications, like diagnostic equipment.

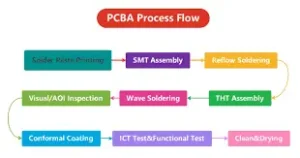
How SMT and THT Components Are Mounted
SMT: Surface Mounting
-
Components are soldered directly onto the PCB surface using automated processes like pick-and-place machines and reflow soldering.
-
Ideal for: Mass production of small, lightweight devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearables.
THT: Through-Hole Mounting
-
Components are inserted into pre-drilled holes in the PCB and soldered from the other side.
-
Ideal for: Applications requiring mechanical strength, such as industrial machinery and aerospace equipment.
Repairability: Easier Access with THT
- THT: Easier to repair and prototype because components are accessible. Ideal for testing and customization.
- SMT: Requires specialized tools for repair, making it harder and more expensive.
Thermal Performance: Managing Heat in PCB Design
- THT: Better at dissipating heat due to leads that extend through the PCB. Suitable for high-power applications.
- SMT: Requires additional thermal management techniques like heat sinks or thermal vias to avoid heat buildup.
Frequently Asked Questions
SMT mounts components on the PCB surface, enabling compact, high-density designs, while THT involves drilling holes for stronger, more durable connections.
- SMT: Best for high-volume production with cost and space efficiency.
- THT: Suitable for prototypes and high-stress environments like aerospace.
Yes! Many designs use SMT for compact components and THT for high-stress parts to achieve optimal performance and reliability.
- Faster production.
- Lower costs for large volumes.
- Supports double-sided, high-density PCB designs.
Limited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
 Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide
Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide No hidden fees – transparent pricing
No hidden fees – transparent pricing Guaranteed quality with on-time deliver
Guaranteed quality with on-time deliverBuild Your Perfect PCB with Unit Circuits
- No MOQ.
- Fast quotes and delivery.
- Comprehensive quality testing.
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




