Quick Leads
Top 5 Testing Methods for Ensuring High-Quality PCB Assembly
💡 Looking for full-service PCB Assembly?
We offer turnkey solutions from PCB manufacturing to testing.
In the competitive world of electronics manufacturing, ensuring the highest quality for printed circuit boards (PCBs) is critical. A robust testing process can help you detect defects early, reduce production costs, and improve product reliability.
In this article, we’ll explore the top 5 PCB testing techniques that every engineer, manufacturer, and quality assurance manager should understand. Whether you’re working on prototypes or high-volume production, these methods will help you make informed decisions to meet your quality goals.
The Importance of PCB Testing
Testing is an essential part of PCB assembly, ensuring that every connection, solder joint, and component performs as expected. The five most widely used testing methods include:
- In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
- Flying Probe Testing (FPT)
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
- X-Ray Inspection
- Functional Testing (FCT)
Each method has its strengths, challenges, and ideal use cases. Let’s dive deeper into how these techniques work, their benefits, and when to use them.
1. Why is In-Circuit Testing (ICT) Essential for PCB Quality?
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) is one of the most reliable methods for identifying manufacturing defects. It uses a bed-of-nails fixture to test each component on a PCB. By measuring resistances, capacitances, and checking connections, it ensures that all components are functioning correctly.
Benefits:
- High fault detection rate: Identifies up to 98% of defects.
- Fast and repeatable: Ideal for mass production.
- Comprehensive testing: Detects open circuits, shorts, and soldering issues.
Best Applications:
- High-volume production where consistent quality is crucial.
- Situations where rapid testing is necessary to keep up with production speed.
Challenges:
- High setup cost: Fixture creation is expensive, making ICT less practical for low-volume production.
- Inflexibility: Design changes require new fixtures.
Example:
In one of our recent projects, ICT detected faulty resistors before shipment. Early defect detection saved both time and costs, ensuring the customer received reliable products.

2. When Should You Use Flying Probe Testing (FPT) in PCB Assembly?
Flying Probe Testing (FPT) is a more flexible alternative to ICT. Instead of a bed-of-nails fixture, it uses robotic probes to test connections. This method is particularly suitable for prototypes and low-volume production.
Benefits:
- No custom fixtures: Saves on setup costs.
- Flexibility: Adapts to design changes without additional expense.
- Precision: Can test boards with unique or complex designs.
Best Applications:
- Prototyping and low- to medium-volume production.
- Scenarios with frequent design iterations.
Challenges:
- Slower than ICT, as the probes must move to each test point.
- Less accurate for very small components with tight pitches.
Analogy:
Think of FPT as a robotic arm that tests different boards one at a time. It’s perfect if you’re working on small batches or prototypes.
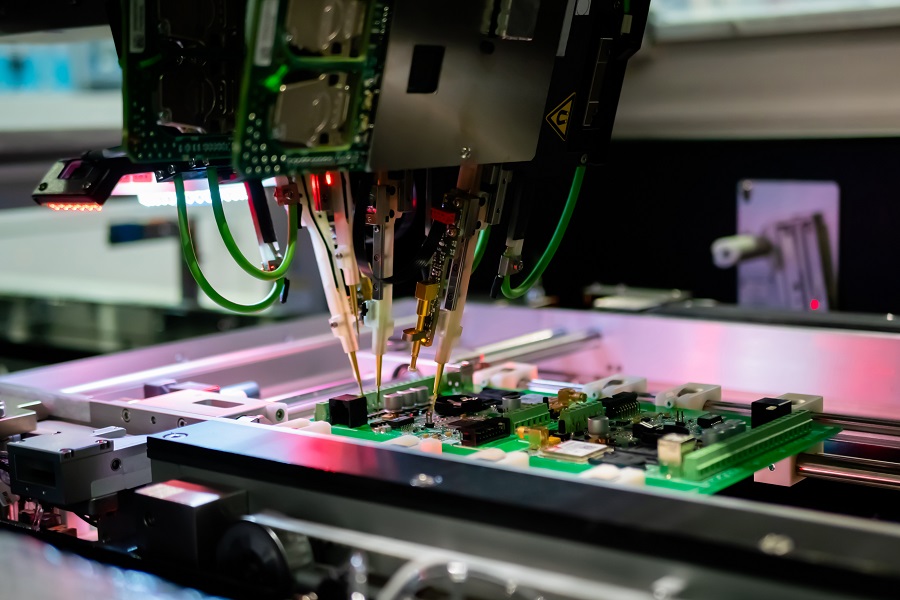
3. How Does Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Improve PCB Quality?
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) uses advanced cameras and imaging technology to detect surface-level defects. By comparing images of your PCB to a reference model, it identifies issues like missing components, incorrect placement, and soldering problems.
Benefits:
- High speed and accuracy: Excellent for inline production inspection.
- Non-contact method: Reduces the risk of damaging delicate components.
- Wide defect coverage: Detects missing parts, solder bridges, and incorrect polarities.
Best Applications:
- Used after solder paste application and component placement to catch defects early.
- Inline inspection during high-speed production.
Challenges:
- Limited to visual defects: Cannot detect internal issues like those in BGAs.
- Requires precise programming for accurate results.
Pro Tip:
AOI is an excellent tool to ensure that components are properly placed and soldered, reducing rework costs further down the production line.

4. Why Use X-Ray Inspection for High-Density PCBs?
X-Ray Inspection allows you to see inside the PCB, making it invaluable for detecting hidden defects, such as voids or soldering issues under BGAs and QFNs.
Benefits:
- Internal defect detection: Perfect for high-density boards with complex designs.
- Detailed imaging: Reveals voids, misalignments, and other issues invisible to AOI.
- Critical for reliability: Often used in aerospace, medical, and other high-stakes industries.
Best Applications:
- Boards with high-density components, like BGAs.
- Situations requiring high reliability, such as aerospace or medical devices.
Challenges:
- High cost: Equipment and skilled operators are expensive.
- Slower process compared to AOI, making it less suited for large-scale production.
Example:
We recently used X-Ray Inspection to identify solder bridges under a BGA. Detecting the problem early prevented costly field failures for our client.
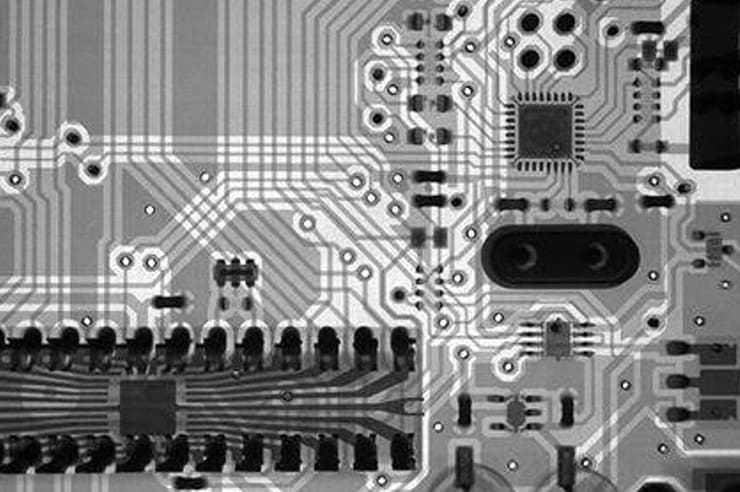
5. What is Functional Testing (FCT) in PCB Manufacturing?
Functional Testing (FCT) verifies the performance of the finished PCB by simulating its real-world operation. It ensures that the board functions correctly in its intended environment.
Benefits:
- Comprehensive testing: Confirms that the PCB meets performance specifications.
- Customizable: Tailored test setups allow simulation of real-world conditions.
- Reliability assurance: Reduces the risk of end-user failures.
Best Applications:
- Final validation before shipment, especially for high-value or complex boards.
Challenges:
- Requires custom setups for each product.
- Testing time can impact throughput for high-volume production.
Pro Tip:
FCT is a must for ensuring that the final product works as expected in its intended environment. It’s often the last line of defense against defects.


Comparison of PCB Testing Methods
Method | Best For | Benefits | Challenges | Cost | Speed |
In-Circuit Testing (ICT) | High-volume production | High fault detection, fast testing | High fixture cost, inflexible | High | Fast |
Flying Probe Testing (FPT) | Prototypes, design changes | Flexible, no fixtures needed | Slower, less accurate for small components | Medium | Slow |
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Inline inspection | Fast, accurate for surface defects | Limited to visual defects | Medium | Fast |
X-Ray Inspection | High-density boards | Detects hidden issues | Expensive, slower than AOI | High | Slow |
Functional Testing (FCT) | Final validation | Thorough functionality checks | Time-consuming, setup-specific | Medium | Varies |
Choosing the Right Testing Method
Selecting the right testing method depends on your project’s requirements, production volume, and budget. For high-volume production, ICT offers speed and reliability. If you’re working on prototypes or low-volume batches, FPT or AOI might be a better fit. For detecting internal defects, X-Ray Inspection is essential, while FCT ensures the final product meets performance expectations.
By understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, you can optimize your PCB assembly process for quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Limited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
Claim your $100 discount now – this offer won’t last long! Today ONLY!
Don’t miss this chance to save on your next project.
[Hurry! Only 50 discounts remaining!]
 Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide
Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide No hidden fees – transparent pricing
No hidden fees – transparent pricing Guaranteed quality with on-time deliver
Guaranteed quality with on-time deliverRequest for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




