Quick Leads
What Are Printed Circuit Boards Made Of? Understanding the Essential Materials and Components
What Are Printed Circuit Boards Made Of?
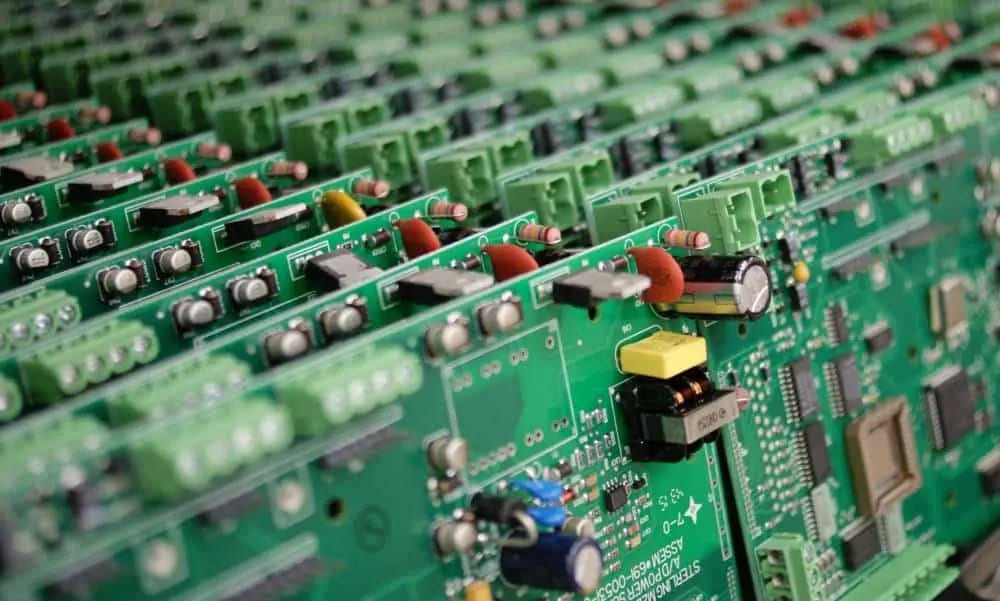
Printed circuit boards, or PCBs, are essential in all modern electronic devices, forming the foundation for connecting different electronic components. Understanding the materials involved in creating a PCB board is vital for any engineer, buyer, or decision-maker involved in sourcing these components.
The materials used in a PCB are designed to perform specific functions. At the basic level, the material structure includes:
- Substrate Materials: This is the base of the PCB, which provides mechanical strength and electrical insulation. Most PCBs use fiberglass reinforced with epoxy resin (FR4). This material is known for its rigidity, strength, and cost-effectiveness. In some applications, polyimide is used as a flexible substrate, ideal for devices that need to bend or flex.
- Copper Layer: The copper layer is essential for the conduction of electrical signals. It’s the part of the PCB that allows components to communicate with each other through pathways etched into the board. Copper is highly favored due to its excellent conductivity.
- Solder Mask: The solder mask layer is a protective covering that prevents accidental solder bridges and protects copper traces from environmental damage like moisture or dust. The solder mask is typically green, but other colors like red, blue, and black can also be used depending on the requirements.
- Silkscreen Layer: The silkscreen is an additional layer on top of the solder mask, used for marking the PCB with component identifiers, logos, or other instructions. This layer doesn’t affect the electrical functionality but is crucial for assembly, repair, and maintenance.
These four primary materials—substrate, copper, solder mask, and silkscreen—make up the standard PCB composition. They come together to form a durable, functional printed circuit board that can support complex electrical connections and ensure the reliability of electronic devices.
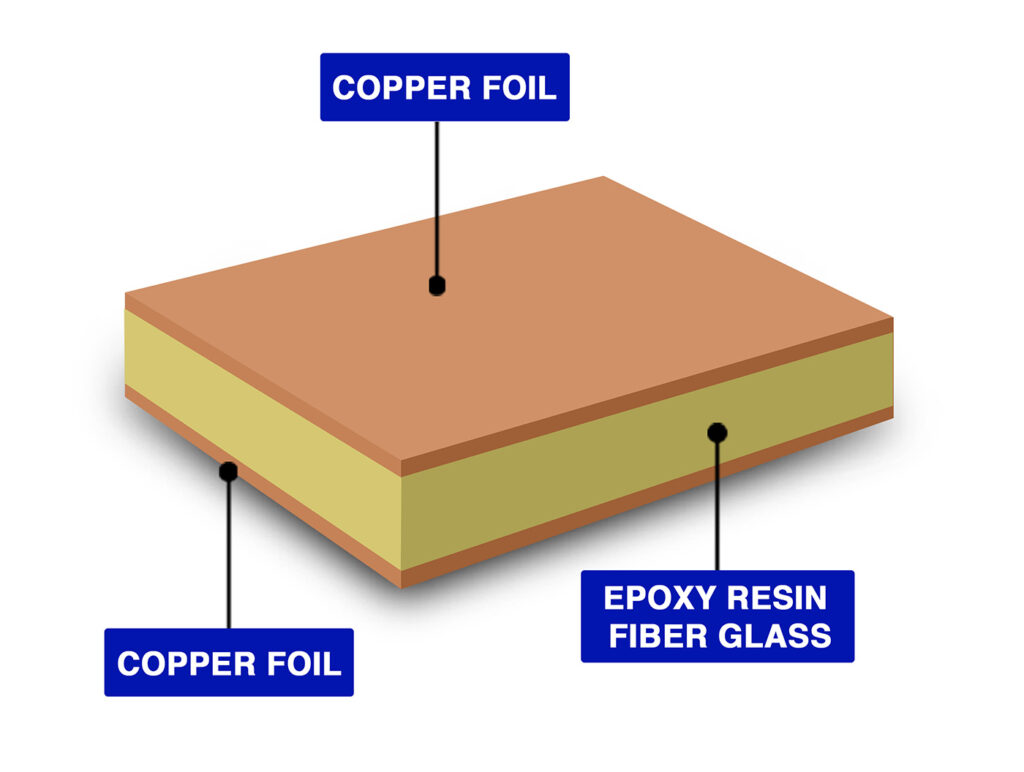
What Material is a Printed Circuit Board Made Of?
What are printed circuit boards made of? The question can be answered in several ways, depending on the type of PCB and its application. However, in general, PCBs are composed of several key materials, each with a specific function:
- Fiberglass and Epoxy Resin (FR4): As the most common PCB substrate material, FR4 combines fiberglass with epoxy resin to form a rigid base. The fiberglass offers strength, while the epoxy resin provides adhesion and insulation. Together, they create a durable, reliable, and cost-effective foundation for PCBs.
- Polyimide: For flexible PCBs, polyimide is often used as the substrate material. Polyimide is a high-performance material that offers thermal stability and flexibility. It is most commonly used in flexible printed circuit boards, which are critical for applications where the circuit board needs to bend or conform to tight spaces.
- Copper: The most common material for the conductive layer of printed circuit boards is copper. Copper traces are etched onto the PCB to create pathways for electricity to flow between components. Copper’s excellent conductivity and reliability make it the most suitable choice for this function.
- Solder Mask: The solder mask serves as a protective layer that helps maintain the integrity of the copper traces. It’s typically made from epoxy or liquid photo-imageable (LPI) material, which is applied over the copper traces to prevent unwanted solder bridges from forming.
- Silkscreen: The silkscreen layer is used to print text or symbols on the PCB, such as component labels, logos, and other helpful markings for assembly. It’s usually made from epoxy ink and is printed over the solder mask.
These materials work together to form a printed circuit board that serves its purpose effectively. Whether it’s a rigid PCB, flexible PCB, or multi-layer PCB, the combination of insulating materials, copper for conductivity, and protective layers ensures that the PCB can withstand both physical and electrical stresses.

What is the Composition of a Printed Circuit Board?
The composition of a printed circuit board can be broken down into the various layers and materials that come together to perform specific functions:
- Copper Layer: This layer is essential for the conduction of electricity and serves as the primary pathway for signals between components. The copper is etched to form the necessary circuit paths.
- Substrate Layer: Made from fiberglass or other composite materials, this insulating layer serves as the base of the PCB, providing mechanical strength and electrical insulation.
- Solder Mask: This layer serves a protective function, preventing solder from creating unwanted electrical bridges between the copper traces and providing resistance against moisture and chemical contamination.
- Silkscreen: A layer used for marking the PCB with text, symbols, and other necessary instructions to guide assembly, troubleshooting, or repairs.
The layers are typically stacked in a way that allows the PCB board to be both functional and durable. Whether it’s a single-sided PCB or a multi-layer PCB, the composition remains relatively consistent, with the copper providing the electrical pathway, the substrate offering structural integrity, and the solder mask and silkscreen layers offering protection and guidance.
Are Printed Circuit Boards Plastic?
While printed circuit boards do contain plastic components, PCBs themselves are not entirely made of plastic. In fact, fiberglass plays a critical role in the construction of PCBs. The plastic components, such as resin or epoxy, are used in the solder mask and silkscreen layers, while the fiberglass forms the substrate material that provides the strength and structure needed for the PCB to hold together.
Most PCBs use a combination of plastic (epoxy resin) and fiberglass to achieve the necessary balance of strength, conductivity, and insulation. Plastic is also used in the form of solder mask, which protects the copper traces from environmental hazards.
Thus, the question “Are PCBs made of plastic?” can be answered with a “yes” for certain components, but it is not the sole material used in their construction. The plastic components serve an essential purpose but are complemented by other materials like fiberglass and copper.
Are PCBs Made of Fiberglass?
Yes, fiberglass is one of the most common materials used in PCB construction. The substrate material, which forms the base of the PCB, is typically made of fiberglass reinforced with epoxy resin. This fiberglass-epoxy composite (FR4) is chosen because of its strength, insulating properties, and cost-effectiveness.
Fiberglass is particularly beneficial because it provides the PCB with the rigidity and mechanical strength required for many types of electronic devices. Moreover, fiberglass is an excellent insulator, preventing short circuits and electrical interference from affecting the performance of the board.
Fiberglass plays a crucial role in the PCB’s thermal management, helping to dissipate heat away from sensitive components. This is particularly important in high-power applications such as LED PCBs or power supply PCBs.
What Are the Common PCB Layers?
Printed circuit boards typically consist of several layers, each serving a unique purpose to ensure the PCB functions effectively. These layers include:
- Substrate Layer: This is the base material of the PCB, usually made from fiberglass or polyimide. It provides mechanical stability and insulation.
- Copper Layer: The copper is etched into the PCB to create the circuit pathways for electric signals to travel between components.
- Solder Mask Layer: The solder mask prevents solder bridges and protects the copper traces from environmental damage. It also ensures the proper functioning of the circuit by preventing unwanted electrical connections.
- Silkscreen Layer: The silkscreen provides visual aids for assembly and maintenance. It typically includes component labels, logos, and other instructions that help technicians assemble and troubleshoot the PCB.
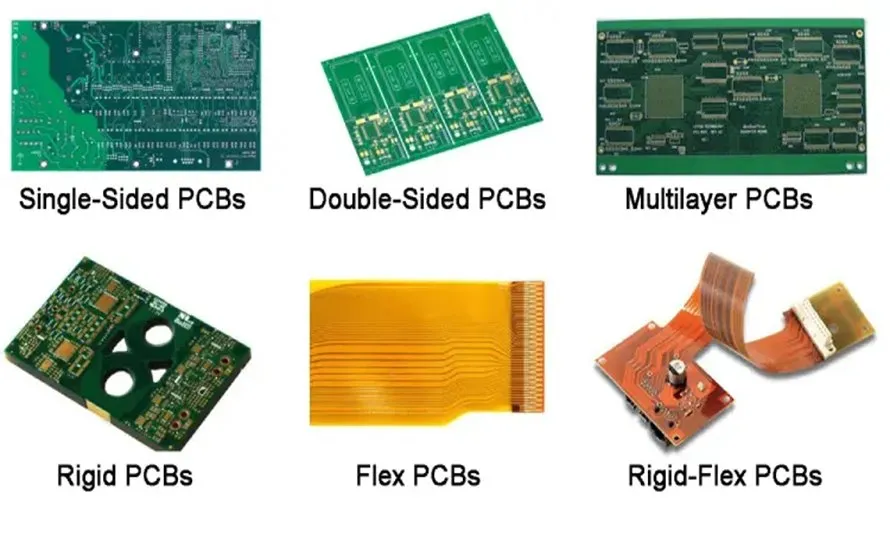
Different Types of Printed Circuit Boards
There are several types of PCBs used in the electronics industry, and each one is made from different materials to suit specific applications:
- Single-Sided PCB: A basic PCB with one layer of conductive copper on one side. Often used in simple devices like calculators or household appliances.
- Double-Sided PCB: A more advanced PCB with copper layers on both sides of the substrate, offering more room for component placement.
- Multi-Layer PCB: A complex design consisting of several layers of copper, used in high-density, high-performance applications like computers and mobile phones.
- Rigid PCB: The most common type of PCB, which uses rigid materials like fiberglass for mechanical strength.
- Flexible PCB: Ideal for compact or mobile devices, these PCBs use polyimide as the substrate and can bend or twist without breaking.
- Rigid-Flex PCB: A hybrid of rigid and flexible PCBs, offering the benefits of both designs in one package.
- HDI PCB: High-Density Interconnect PCBs are used for high-performance devices with fine circuitry and a high number of connections.
- LED PCB: Designed specifically for LED applications, these PCBs use metal-core substrates for better heat dissipation.
- Blank PCB: A PCB without any components, usually used for prototyping or custom circuit designs.
- Custom PCB: These are tailor-made to suit specific requirements, with materials chosen based on the project’s needs.
Materials Used in Printed Circuit Board Substrates
Several materials can be used as substrates in PCBs, depending on the application. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common:
- FR4 (Fiberglass-Reinforced Epoxy Resin): The most widely used PCB substrate due to its strength, affordability, and insulation properties.
- Rogers: Used for high-frequency applications, such as radar systems and communication devices. It offers excellent signal integrity.
- Metal-Core: Typically used in LED PCBs, this substrate has a metal layer (such as aluminum) for heat dissipation.
- Polyimide: Used in flexible PCBs, polyimide offers high thermal resistance and the ability to bend without cracking, making it ideal for portable electronics.
How to Select the Right Printed Circuit Board Material?
Choosing the right PCB material depends on several factors, including the application, environment, and performance requirements. Consider the following when selecting your PCB material:
- Application: Different applications require different materials. For example, high-speed communication devices might require Rogers material, while LED applications may demand metal-core materials.
- Temperature: Some materials are better suited for high-temperature applications. If your device operates in extreme conditions, choose a material that can withstand these stresses.
- Flexibility: For devices requiring bending or twisting, polyimide (for flexible PCBs) is the ideal choice.
- Cost: Depending on your budget, you may need to balance the need for high-performance materials with cost-effectiveness.
Understanding the properties of each material allows you to select the best material for your specific printed circuit board design.
Limited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
 Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide
Trusted by 100+ businesses worldwide No hidden fees – transparent pricing
No hidden fees – transparent pricing Guaranteed quality with on-time deliver
Guaranteed quality with on-time deliverConclusion
Choosing the right printed circuit board material is essential for ensuring the efficiency, reliability, and longevity of your electronic devices. By understanding the various PCB materials and how they work together, you can make better decisions when sourcing printed circuit boards.
For more information, feel free to explore our resources or contact us for any PCB design needs you may have.
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




