Quick Leads-PCBA
Sourcing PCB assembly in 2025 means more than just picking a vendor — it means balancing cost, compliance, and reliability. One of the first decisions you’ll face? Lead vs. lead-free solder. Here’s what we’ve learned as a turnkey PCB assembly provider working with thousands of global clients.
Lead solder offers easier processing and smoother joints but poses environmental and compliance issues under RoHS and REACH. Lead-free solder, while slightly costlier and harder to work with, meets global regulations and offers better joint strength and reliability in harsh environments. Choosing between them depends on application type, market compliance needs, and your assembly partner’s capability.
So how do you decide what’s best for your next build — especially under tighter timelines, stricter compliance, and rising material costs? Let’s break it down clearly.
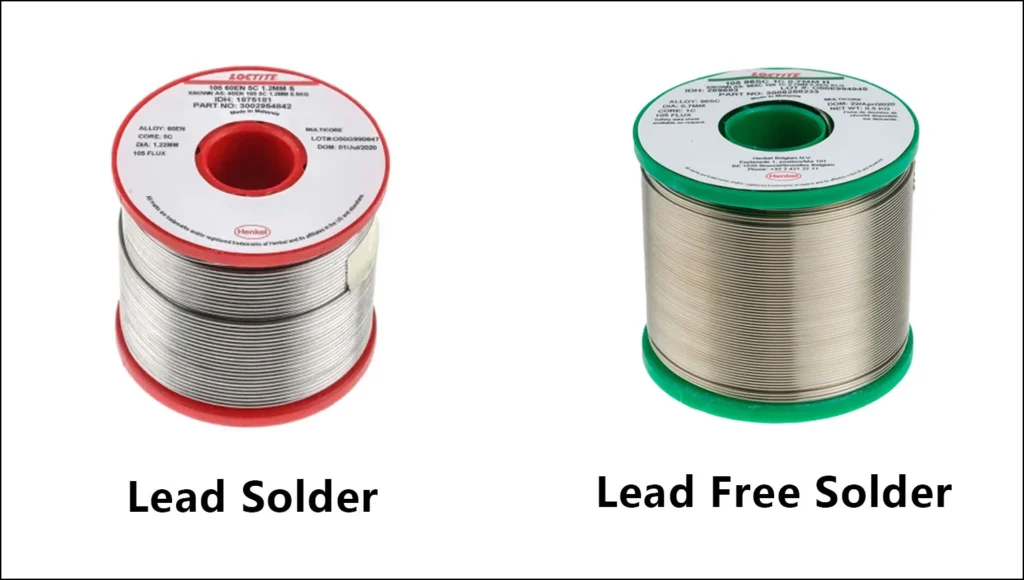

🔧 What is the Difference Between Lead and Lead-Free Solder?
The difference between lead and lead-free solder goes beyond just the presence of lead. It’s about how the solder performs, what standards it meets, and how well it integrates into your specific manufacturing process.
📦 Composition & Alloy Breakdown
-
Lead Solder: Typically 63% tin and 37% lead (Sn63/Pb37), this eutectic blend has a sharp melting point.
-
Lead-Free Solder: Often SAC305 (96.5% tin, 3.0% silver, 0.5% copper), though variants exist based on specific applications.
🌡 Melting Point Comparison
Lead-free solders melt at 217–221°C, much higher than leaded solder’s 183°C. That extra heat can stress sensitive components if your thermal profile isn’t dialed in.
🧪 Physical Characteristics
Lead solder flows better and leaves shiny joints. Lead-free joints may appear dull or grainy but are mechanically stronger.
The temperature and handling differences between leaded and lead-free solder are especially important in RoHS-compliant builds, as outlined in this DigiKey guide.
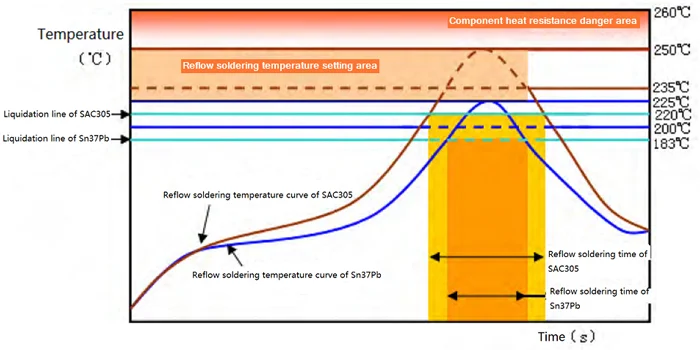
📊 Comparison Chart: Lead vs. Lead-Free Solder Properties
| Property | Lead Solder (Sn63/Pb37) | Lead-Free Solder (SAC305) |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 183°C | 217–221°C |
| Joint Appearance | Smooth, shiny | Dull, grainy |
| RoHS Compliant | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Cost per kg | Lower | Higher |
| Fatigue Resistance | Higher | Slightly lower |
| Suitable for Harsh Environments | Moderate | High |
💡 Is Lead-Free Solder Better for PCB Assembly?
The short answer? It depends on your product and target market.
We’ve worked with everything from automotive electronics to consumer IoT and medical devices, and each use case demands something different.
✅ When Lead-Free Is Better:
Regulated Markets: RoHS and REACH restrict lead in electronics, especially for products sold in the EU, Japan, and parts of North America.
High-Stress Applications: SAC305 offers better mechanical strength and reliability in humid or vibrating environments.
Green Branding: Products labeled “lead-free” can be a selling point in eco-conscious markets.
🧯 Reliability Factors
Lead-free solder can handle thermal cycling and mechanical stress better in some cases, especially when designed with proper thermal profiles and pad geometries.
Unit Circuits: Leading PCBA Manufacturer
 ISO-certified & 8+ years of PCBA
ISO-certified & 8+ years of PCBA Low MOQ & Fast Turnaround
Low MOQ & Fast Turnaround Prototype & Mass production
Prototype & Mass productionLimited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!

🤔 Can I Use Leaded Solder for PCB Assembly in 2025?
This is a common question, especially from engineers working in industrial or legacy product lines.
❗ Where Lead Solder is Still Used:
-
Defense & Aerospace: Many military applications are exempt from RoHS. Leaded solder is preferred for its predictable rework and reliability under mission-critical conditions.
-
Prototyping: Leaded solder is often easier to work with on a bench — it flows better and is forgiving of minor errors.
-
Internal Use: If the product won’t leave your facility or be sold commercially, leaded solder might be acceptable.
But beware — even small-scale use of leaded solder requires disposal procedures and worker safety protocols.
🔍 Compliance Matters
-
RoHS bans lead content above 0.1% in most electronics.
-
WEEE (EU) and REACH (global) reinforce this across the supply chain.
-
Even OEMs sourcing from Asia are tightening compliance.

🔩 Leaded vs. Lead-Free: Which is the Best Solder for PCB Assembly?
Let’s break it down based on your industry and priorities:
📊 Application Fit: Leaded vs. Lead-Free by Industry
| Industry | Recommended Solder | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Lead-Free | RoHS Compliance |
| Aerospace | Lead-Free | High-Reliability |
| Industrial Control | Either | Performance Priority |
| Prototyping | Leaded | Ease of Rework |
| Medical Devices | Lead-Free | Bio-Safe, Regulatory |
| Military | Leaded (Exemptions Apply) | IPC Standard Flexibility |
We typically recommend SAC305 for most clients due to its compliance and reliability in production. But if you’re prototyping, troubleshooting, or dealing with tight thermal budgets, Sn63/Pb37 may still have a place.
Choosing between solder types isn’t just about performance — it also comes down to budget. Lead-free alloys can be more expensive due to material and process requirements. For a deeper dive into how these and other factors influence project costs, check out our guide on the 10 key factors that affect PCB assembly pricing.
🌱 Why Use Lead-Free Solder in Electronics Manufacturing?
There’s more at stake than just rules. Lead-free solder is a move toward greener electronics manufacturing and fewer health hazards.
🌍 Environmental and Health Safety
-
Lead-free solder reduces toxic waste, especially in landfills.
-
Safer for operators during reflow, inspection, and rework.
-
Cleaner factory environments — especially when combined with low-residue flux options.
🏷 Meets Global Standards
-
RoHS (EU): Restricts hazardous substances including lead.
-
REACH: Broader chemical safety regulation.
-
WEEE: Electronic waste handling rules.
-
IPC Standards: Especially IPC-A-610 for acceptable solder joints and assemblies.

🔧 Technical Challenges in Lead-Free PCB Assembly (And How We Solve Them)
Here’s where experience matters. Lead-free solder can be tricky — but we’ve solved it many times over.
🔥 Higher Reflow Temperature
Components must tolerate +30–40°C more heat. We solve this with:
-
DFM checking to validate parts before sourcing
-
Thermal profiling during reflow to prevent delamination
-
Board stackup adjustment to minimize warping
💥 Common Issues with Lead-Free Solder
-
Tombstoning of small passives
-
Incomplete wetting
-
Voiding in BGAs
-
Flux residue affecting test points
🛠 Our Fixes Include:
-
Optimized paste printing and stencil design
-
Proper SAC305 alloy selection for your board’s design
-
Advanced cleaning processes post-soldering
These are problems we see and solve every week — especially for clients requiring quick turn lead-free PCB assembly in low-volume/high-mix builds.
Handling higher reflow temperatures in lead-free PCB assembly takes precise profiling and well-matched components. We follow IPC best practices and recommend reviewing these reflow soldering tips to help avoid warping, tombstoning, or solder joint voids in your next SMT project.
🔄 How We Support Clients With Low-Cost, RoHS-Compliant PCB Assembly
Even lead-free solder can be affordable — if your assembler is set up for it. Here’s how we help:
🚀 Fast Turnaround & Zero MOQ
-
No MOQ PCB assembly in China: Ideal for startups or NPI
-
Fast quoting in under 4 hours
-
Global sourcing + verified substitutes for hard-to-find components
🧰 End-to-End Process
-
DFM + DFA analysis before soldering starts
-
Reflow profiling tailored to your board and solder type
-
Functional testing and AOI/ICT to catch faults early
-
Final box-build and logistics (if needed)
Whether you need 5 boards or 5,000 — we’re ready to deliver.
FAQs
1. Why is lead-free solder so expensive compared to leaded solder?
Lead-free solder often contains pricier metals like silver and copper (e.g., SAC305), which increase material costs. Additionally, manufacturing with lead-free alloys requires higher reflow temperatures and tighter process control, adding to production complexity. These factors contribute to why lead-free solder for electronics is more expensive than traditional tin-lead blends.
2. What is the lead-free solder law and how does it affect my product?
The lead-free solder law refers primarily to RoHS and REACH regulations, which restrict hazardous substances in electronics — including lead above 0.1%. If you're exporting to the EU or many global markets, your PCB assembly must use RoHS compliant solder to pass inspection and avoid penalties.
3. How can I tell if a solder joint is lead-free or leaded?
Lead-free solder joints usually appear duller and grainier, while leaded joints look shiny and smooth. To be sure, check the solder reel label or request a material declaration from your PCB assembly supplier. Many RoHS compliant PCB assemblies also include certification labels during shipping.
4.Why is lead-free solder harder to work with in prototyping?
Lead-free solder has a higher melting point (around 217°C+), making it less forgiving during rework or manual soldering. It also has lower wetting characteristics, which can lead to inconsistent joints if not properly handled. That’s why many engineers still prefer leaded solder for bench-top prototypes, despite compliance tradeoffs.
Have Specific Requirements?
Looking for high-precision PCB assembly for your products? Our team specializes in delivering top-tier assembly services, ensuring your devices perform flawlessly in any environment. Contact us today for a free consultation on how we can enhance your product’s reliability.
🧭 Key Takeaways: Lead-Free vs. Leaded — How to Make the Right Decision
Here’s how we usually help clients navigate this choice:
-
If you’re selling to the EU or big-box retailers? You need lead-free.
-
Need high-reliability joints in harsh environments? Lead-free wins again.
-
Just prototyping or building internal tools? Leaded solder could save you some headaches.
📌 But don’t guess. Our engineers work with you directly — one-on-one — to choose the right alloy, process, and inspection flow. That’s the power of a true turnkey PCB assembly service.
📢 Ready to Build? Let’s Talk
Choosing the right solder is critical to performance, compliance, and cost. Whether you’re building medical devices or IoT prototypes, we help you find the best-fit solution. Got a project? Request a fast, free quote → — our team is ready to help you make the smart choice.
Save on your next PCB project?
Claim $100 OFF your order today.
✅ high-quality PCB assembly with strict quality control ✅ ISO-certified & 8+ years of experience. ✅ Low MOQ, fast turnaround, and 100% E-tested PCBs.
Additional Resources:
- How to Repair Circuit Boards: A Step-by-Step Beginner’s Guide
- Capacitor on Circuit Board: A Comprehensive Guide
- What Are PCB Conformal Coatings? Types, Benefits, and Applications Explained
- SMD Size Codes Explained: A Complete Guide to Understanding Surface-Mount Component Dimensions
- AC vs DC: Key Differences, Applications, and Advantages in Modern Electronics
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




