Quick Leads-PCBA
Many electronics manufacturers face tough choices: stick with reliable leaded solder or switch to lead-free for RoHS compliance. But does going green mean sacrificing performance? Choosing the wrong solder impacts reliability, cost, and compliance. Let’s break down the facts to help you make smarter sourcing decisions.
Leaded solder joints generally offer better mechanical reliability, with higher ductility and lower thermal fatigue risk. In contrast, lead-free solder joints—though RoHS-compliant—tend to have higher failure rates under drop testing and thermal cycling. Still, newer alloys like SAC305 have closed this gap, making lead-free viable for many applications.
Still wondering which solder to choose for your project? Let’s explore each type’s technical performance, reliability trade-offs, and how real-world constraints influence sourcing decisions.
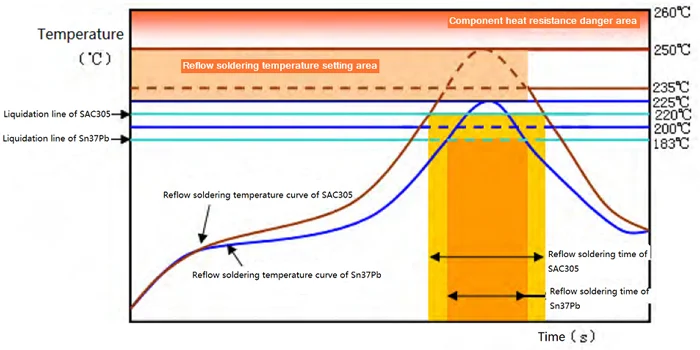
🔧 Is lead solder better than lead-free solder?
This is probably the most asked question in electronics manufacturing—and for good reason. Leaded solder (usually Sn63/Pb37) is easier to work with, especially during manual soldering or rework. It flows beautifully, creates smooth, shiny joints, and has a lower melting point (183°C). Technicians love it.
Lead-free solder, especially alloys like SAC305 or Sn100C, has a higher melting point (typically 217–227°C), and the wetting is just not the same. It often results in dull-looking joints and demands tighter control of thermal profiles.
Still, for many applications, especially high-volume manufacturing, lead-free has become the standard—mostly because of RoHS compliance. If you’re building consumer electronics or exporting to the EU, you don’t really have a choice.
🔍 What is the difference between lead and lead-free solder joints?
Here’s a high-level breakdown of their physical and chemical behavior:
📊 Physical & Technical Differences
| Property | Leaded Solder (Sn63/Pb37) | Lead-Free Solder (SAC305 / Sn100C) |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 183°C | 217–227°C |
| Wetting Performance | Excellent | Moderate to poor |
| Joint Appearance | Shiny, smooth | Dull, matte |
| Soldering Ease | Easier | Requires higher skill/temp |
| Flux Requirement | Lower | Higher |
| Oxidation Rate | Lower | Higher |
| Environmental Compliance | ❌ Not RoHS compliant | ✅ RoHS compliant |
From a pure usability standpoint, leaded solder wins. But when you zoom out and consider regulations, toxicity, and future-proofing your process—lead-free solder becomes harder to ignore.

📉 Does lead-free solder affect reliability?
Yes, it absolutely can.
Most of us working with PCB assembly know that drop reliability, thermal fatigue, and vibration resistance are serious concerns—especially for automotive and aerospace.
-
Leaded solder is more ductile, meaning it can flex under stress before breaking.
-
Lead-free solder tends to be brittle, leading to higher failure rates in drop tests and thermal cycling.
-
Lead-free also suffers from tin whiskers—those sneaky metallic fibers that can grow over time and cause shorts.
There’s a reason some aerospace manufacturers still use SnPb in mission-critical assemblies.
According to IEEE research on lead-free solder reliability, lead-free alloys present unique challenges in stress conditions compared to leaded solder.
📊 Reliability Under Stress
| Test Category | Leaded Solder | Lead-Free Solder |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test (Mobile) | ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
| Vibration (Auto) | ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
| Thermal Cycling | ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
| Tin Whisker Risk | ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️ |
| Long-term Aging | ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ | ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
That said, modern alloys like SAC305 and Sn100C have come a long way. When used correctly with controlled profiles, they offer good enough reliability for most consumer and industrial applications.
Unit Circuits: Leading PCBA Manufacturer
 ISO-certified & 8+ years of PCBA
ISO-certified & 8+ years of PCBA Low MOQ & Fast Turnaround
Low MOQ & Fast Turnaround Prototype & Mass production
Prototype & Mass productionLimited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!

🧑🔬 Why is lead-free solder used if it’s worse?
Simple answer: Regulations.
The EU’s RoHS directive (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and other similar global regulations ban the use of lead in most electronic products. So, even if leaded solder is better for reliability, you often can’t use it legally.
Moreover, lead is toxic. Long-term exposure is hazardous to both people and the environment. Lead-free soldering isn’t just about compliance—it’s also about corporate responsibility.
So even if the lead-free solder reliability is slightly lower, companies prioritize:
-
Legal compliance
-
Eco-friendliness
-
Customer trust
And honestly? With modern reflow ovens, nitrogen environments, and careful process control, you can achieve excellent results with lead-free solders.
Due to RoHS regulations, lead-free solder has become the standard in global markets—even though it may pose technical trade-offs. Here’s how RoHS-compliant solder affects PCB reliability and market access.
♻️ Thermal fatigue & long-term durability in solder joints
This is where things get really technical.
In real-world electronics, solder joints face thermal cycling: the PCB heats up and cools down repeatedly. This causes expansion and contraction. Over time, this stress can cause cracks, especially in lead-free solder joints.
The issue is worse in:
-
Power supplies
-
Automotive under-hood electronics
-
Outdoor devices exposed to temperature swings
Leaded solder handles thermal fatigue better. Its ductility lets it flex, while lead-free is more prone to micro-cracks.
Some manufacturers combat this by:
-
Adding silver or bismuth to the alloy
-
Using underfill in BGA packages
-
Optimizing pad design to distribute stress
So if your product will live in a high-stress thermal environment, it’s worth reconsidering your solder choice or investing in more robust assembly processes.
Even with the right solder alloy, long-term PCB reliability depends heavily on joint quality and inspection. Explore proven methods to detect and prevent soldering defects in PCB assembly to mitigate these risks.
💧 Solder wetting, voiding, and visual standards
Ask any soldering technician what annoys them the most, and they’ll probably say: wetting issues.
-
Leaded solder wets easily.
-
Lead-free solder often shows poor wetting, incomplete fills, and dull finishes.
This affects not just the joint quality but also your pass rate for IPC-A-610 inspections. Especially if you’re aiming for Class 3 (High Performance Electronics), this becomes a real bottleneck.
As outlined in IPC’s inspection guide for lead-free assemblies, the visual characteristics differ significantly from leaded joints, often affecting pass/fail judgments.
Common issues with lead-free:
-
Voiding inside joints
-
Incomplete fillets
-
Cold joints from insufficient heat transfer
Engineers can mitigate this with:
-
Better thermal profiling
-
Nitrogen reflow ovens
-
Optimized pad design and stencil apertures
Still, this is one reason some OEMs quietly prefer leaded solder for prototypes and small runs, where visual standards are critical.
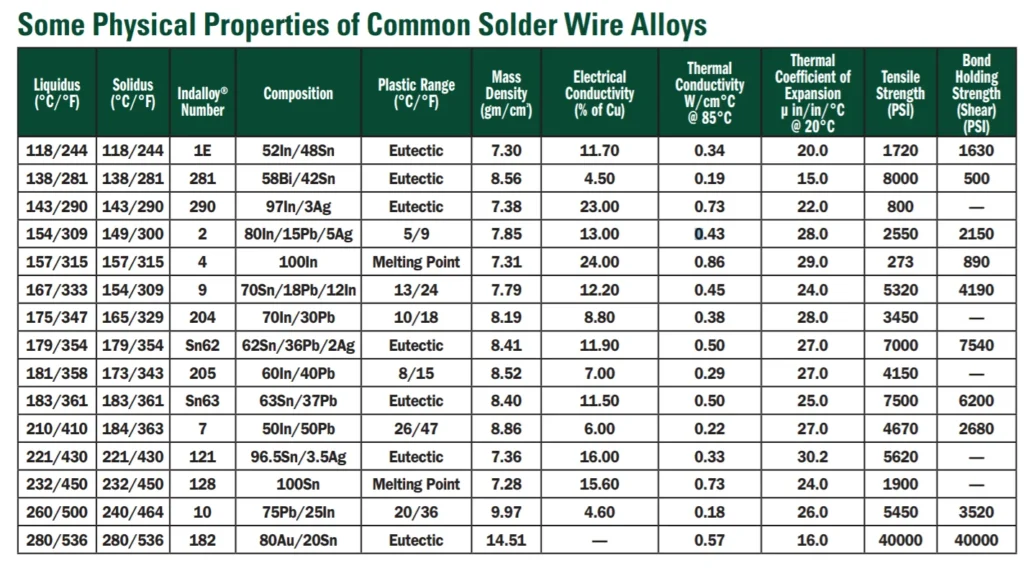
🌡️ Leaded solder melting point vs lead-free
Another simple but critical difference: melting temperature.
-
Leaded solder (Sn63/Pb37): 183°C
-
SAC305 (lead-free): ~217°C
-
Sn100C (lead-free): ~227°C
This has real-world implications.
-
You need hotter ovens, which can stress components.
-
Components need to be RoHS-ready (not all are!).
-
PCBs with fine-pitch ICs or multiple layers may warp under high temp.
If your board includes temperature-sensitive parts or hasn’t been re-qualified for RoHS, this can become a production risk.
🧪 What’s the best solder type for prototyping PCBs?
I get this question a lot, especially from engineers trying to balance budget, speed, and quality.
For prototyping, the priority is ease of soldering and clean joints. And that’s where leaded solder wins:
-
Lower melting temp = less thermal shock
-
Better wetting = fewer rework issues
-
Easier inspection (shinier joints)
That said, if you’re planning to scale to mass production in a RoHS environment, it’s better to prototype using lead-free—to avoid surprises.
FAQs
1. Can you mix lead-free and leaded solder on the same PCB?
Technically, you can—but it’s not recommended. Mixing solder types can create inconsistent melting points, unpredictable solder joint reliability, and inspection issues. It also violates RoHS compliance if the final assembly is sold in regulated markets. If you must rework a lead-free PCB with leaded solder, it’s critical to document the process and check compatibility with IPC-A-610 solder standards.
2. Why is lead-free solder more expensive than leaded solder?
Lead-free solder contains metals like silver, copper, and bismuth, which are more expensive than lead-tin alloys. The higher melting point also demands better tools and more energy during PCB assembly, adding to production costs. Additionally, RoHS-compliant solder for PCB assembly often requires specialty flux and tighter process control, which further increases the cost of switching to lead-free soldering.
3. Does lead-free solder require special flux or soldering tools?
Yes. Because of its higher melting point and oxidation rate, lead-free solder typically requires active flux formulations and stronger thermal profiles. Using the same setup as for leaded solder PCB work often leads to poor wetting and cold joints. Many assemblers use preheated tips, nitrogen atmospheres, or reflow ovens with tuned profiles to handle lead-free soldering reliably.
4. How do I know if my solder is lead-free or not?
Most lead-free solder wires are labeled as such and often have distinctive color codes (e.g., green spools). You can also check the alloy code—SAC305, Sn100C, and similar codes indicate lead-free solder alloy types. If in doubt, request a material safety data sheet (MSDS) from your supplier or look for RoHS markings on the packaging to confirm compliance.
Have Specific Requirements?
Looking for high-precision PCB assembly for your products? Our team specializes in delivering top-tier assembly services, ensuring your devices perform flawlessly in any environment. Contact us today for a free consultation on how we can enhance your product’s reliability.
🚨 Industry pain points and how we solve them
Here’s the part no one talks about: even with the best materials, most soldering problems come from process control. We hear it all the time:
-
“Our joints are cracking after 6 months!”
-
“Drop testing keeps failing!”
-
“We switched to lead-free and now we have 10% voiding!”
Here’s how we address these issues in our PCB assembly services:
✅ Our Solutions
| Pain Point | Our Solution |
|---|---|
| Tin whiskers and brittle joints | Use SAC305 + bismuth blends with underfill where needed |
| Thermal fatigue failures | Reflow profiling & thermal stress simulation |
| Voiding & cold joints | Nitrogen reflow + IPC-trained operators |
| Solder crack failures in automotive | Pre-qualification of alloys under thermal cycling |
| IPC-A-610 Class 3 visual failures | Visual QC + x-ray + AOI inspection standards |
We’re not just “RoHS compliant”—we’re reliability-first. Our engineers collaborate with clients from layout to final reflow, ensuring you don’t just pass inspection—but stay functional in the field.
✅ Summary
Choosing between leaded and lead-free solder affects your product’s performance and compliance. Still unsure? Our engineers can help you select the right alloy for your application. Let’s build something reliable—together.
Save on your next PCB project?
Claim $100 OFF your order today.
✅ high-quality PCB assembly with strict quality control ✅ ISO-certified & 8+ years of experience. ✅ Low MOQ, fast turnaround, and 100% E-tested PCBs.
Additional Resources:
- How to Repair Circuit Boards: A Step-by-Step Beginner’s Guide
- Capacitor on Circuit Board: A Comprehensive Guide
- What Are PCB Conformal Coatings? Types, Benefits, and Applications Explained
- SMD Size Codes Explained: A Complete Guide to Understanding Surface-Mount Component Dimensions
- AC vs DC: Key Differences, Applications, and Advantages in Modern Electronics
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




