Quick Leads-PCBA
Switching to lead-free solder PCB manufacturing sounds simple, but it rarely is. Engineers and procurement teams face higher melting points, thermal stress issues, and tighter quality demands—without always knowing if the trade-off is worth it. Let’s unpack the real challenges—and smart solutions.
Lead-free solder significantly affects PCB manufacturing by increasing the soldering temperature (217–221°C for SAC305), introducing new quality risks (like thermal stress and tin whiskers), and raising production costs. However, it’s required for RoHS compliance and offers environmental advantages. Manufacturers need optimized reflow profiles, solid inspection protocols, and experience with RoHS processes to maintain quality and control costs effectively.
But if you’re making decisions about lead-free PCB assembly, there’s more at stake than just heat curves and regulations—let’s get into the real engineering behind the scenes.
🔍 What’s the Melting Point of Lead-Free Solder and Why It Matters?
Lead-free solder—particularly SAC305 solder alloy, which consists of tin-silver-copper solder—melts at 217–221°C. That’s a 30–40°C jump compared to traditional Sn63Pb37 solder (which melts at 183°C).
This higher melting point isn’t just a number—it changes how everything works on the line:
-
It affects temperature curve for lead-free solder reflow ovens.
-
It pushes thermal stress on sensitive components.
-
It increases energy consumption during soldering.
If your assembly line isn’t calibrated with a precise lead-free solder temperature profile for SAC305, expect trouble. Warping, delamination, and even latent failures aren’t uncommon.
🔧 How Does Lead-Free Solder Affect PCB Quality?
There’s a reason many engineers still whisper, “lead-free solder is harder to work with.” It’s not just nostalgia.
Here’s what we see in practice:
-
Lower wettability: joints don’t “flow” as nicely.
-
Increased risk of PCB delamination: due to longer dwell times at higher temps.
-
Micro-cracks and tin whiskers: especially under cyclic temperature conditions.
-
Higher failure rates in high-reliability sectors unless proper reflow profiles and inspection systems are in place.
🔍 Common Quality Pitfalls
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Dull Solder Joints | Poor wetting of lead-free alloys | Improve flux chemistry and preheat zones |
| Delamination | Higher peak reflow temperatures | Use low-CTE laminate and correct ramp-up rate |
| Cold Joints | Improper SAC305 profile | Calibrate reflow oven by board type |
So, how does lead-free solder affect PCB quality? If you don’t design around its properties, the answer is: dramatically.
And since lead-free solder joints are more prone to micro-cracks and dull finishes, having solid inspection protocols becomes non-negotiable. You can explore the top 5 testing methods for ensuring high-quality PCB assembly to see how proper QA offsets these risks.
Unit Circuits: Leading PCBA Manufacturer
 ISO-certified & 8+ years of PCBA
ISO-certified & 8+ years of PCBA Low MOQ & Fast Turnaround
Low MOQ & Fast Turnaround Prototype & Mass production
Prototype & Mass productionLimited Time Offer:
Get $100 off your order TODAY!
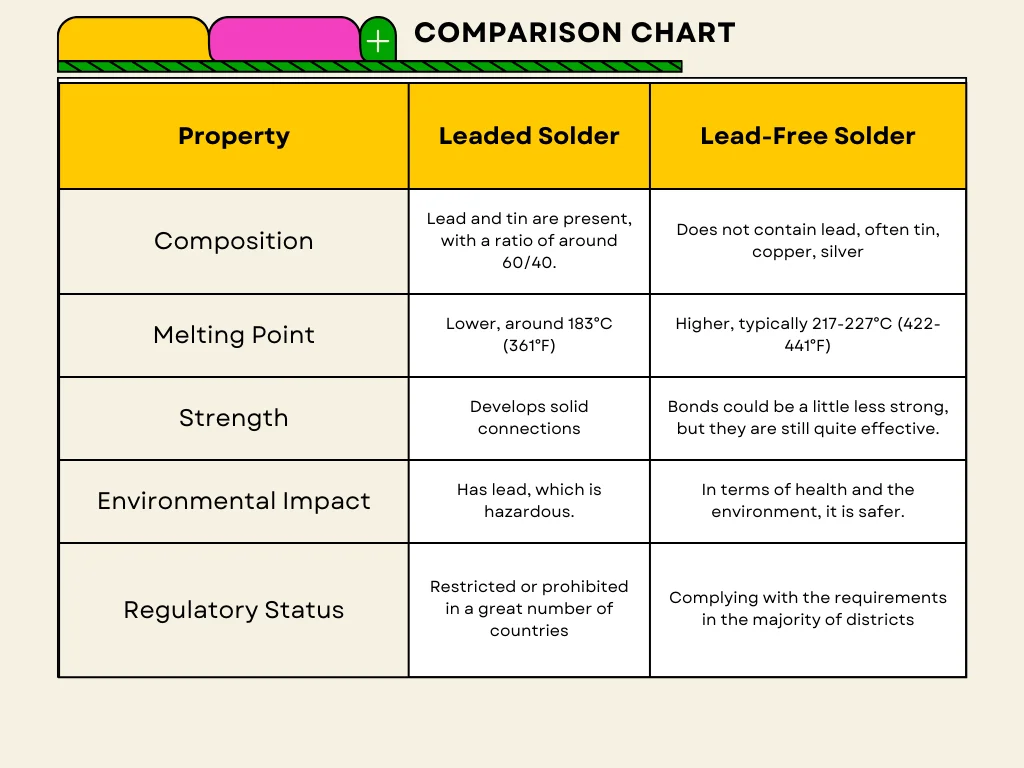
📊 Lead vs Lead-Free: A Straightforward Comparison for PCB Manufacturing
Let’s break it down visually for faster decisions.
📈 Lead vs Lead-Free in PCB Manufacturing
| Property | Leaded Solder (Sn63Pb37) | Lead-Free Solder (SAC305) |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 183°C | 217–221°C |
| Wetting Quality | High | Moderate |
| RoHS Compliant | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Appearance | Shiny | Matte |
| Cost of Material | Lower | Higher |
| Process Control Sensitivity | Moderate | High |
| Environmental Impact | High (toxic lead) | Low |
It’s not about which is better—it’s about which is right for your product and market.
💰 The True Cost of Lead-Free PCB Assembly (Not Just Dollars)
A lot of decision-makers focus on BOM costs. But when switching to PCB manufacturing with lead-free solder, that’s only one slice of the pie.
💸 Hidden Cost Drivers
-
Reflow profile tuning: takes real engineering time.
-
Material selection: not all PCBs or parts are lead-free capable.
-
Inspection overhead: AOI must detect subtler solder faults.
-
Component sourcing: RoHS-certified sourcing is slower and costlier.
At our facility, we maintain RoHS-compliant assembly and offer real-time traceability of solder paste lots, component batches, and reflow settings. That means you’re not paying for trial-and-error; you’re buying repeatability.

🇨🇳 RoHS-Compliant PCB Assembly Manufacturer in China: What to Look For
You’re sourcing from China—great. But RoHS-compliant PCB assembly manufacturer China isn’t a badge every shop earns equally.
✅ Checklist:
-
Uses lead-free solder paste like SAC305 with full spec traceability.
-
Offers certified reflow temperature profiling services.
-
Maintains IPC-A-610 standards for visual inspection.
-
Handles component sourcing for lead-free PCBs without delays.
-
Provides real-time SPC data to validate quality claims.
We do all of the above—and still meet aggressive lead times.
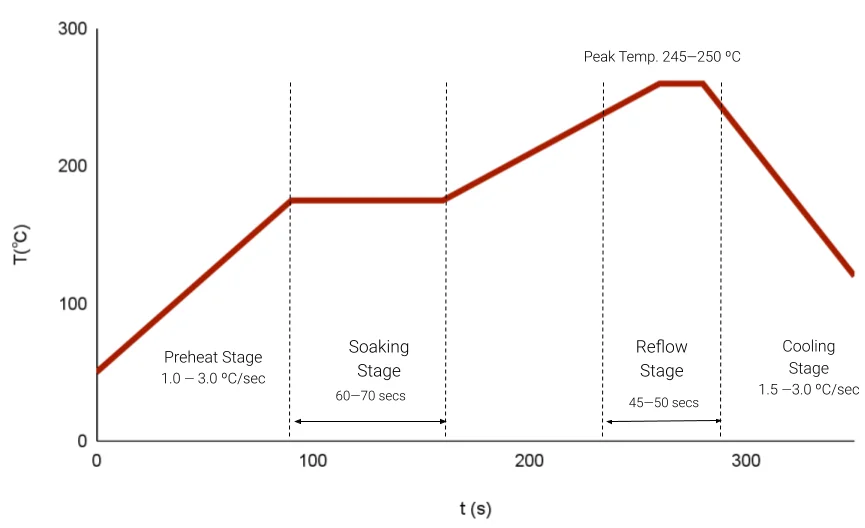
🔥 Best Reflow Profile for Lead-Free Solder Like SAC305
You can’t talk about lead-free solder PCB reliability without diving into the reflow profile. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
📋 Key Specs for SAC305:
-
Ramp Rate: 1.0–3.0°C/sec
-
Peak Temp: 240–250°C
-
Time Above 217°C: 60–120 sec
-
Cooling Rate: 2.0–4.0°C/sec
If your best reflow profile for lead-free solder doesn’t match your board’s thermal mass, you’re toast—literally. Components can lift, crack, or cold-joint.
We profile every batch—whether it’s 10 boards or 10,000.
If you’re using SAC305, be sure to match your reflow profile to manufacturer recommendations—like those found in the MG Chemicals SAC305 solder wire datasheet—to avoid cold joints or overheating components.

📦 PCB Assembly with No MOQ: How Lead-Free Options Work for Small Batches
Running a low-volume order with lead-free solder shouldn’t mean lower quality.
We support PCB assembly no MOQ lead-free solder by:
Pre-calibrated reflow zones for batch sizes.
Flux chemistries optimized for both wave and selective soldering.
Modular stencil and pick-and-place processes to save tooling cost.
This flexibility is especially helpful for:
Hardware startups testing new designs
Medical or automotive prototypes requiring RoHS compliance
Engineers validating thermal cycling behavior before scaling
Whether you’re building 10 or 10,000 boards, we make no-MOQ lead-free solder assembly easy and reliable. See how we handle fast, RoHS-ready prototyping in our dedicated no-MOQ PCB assembly service page.
⚡ Speed vs Quality: Fast Lead-Free PCB Assembly Services Without Compromise
Speed kills—unless you control it.
Here’s how we provide fast lead-free PCB assembly services without risking quality:
📉 Speed vs Quality Trade-offs & Solutions
| Speed Driver | Risk | Our Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Quick Reflow | Cold joints | Automated profile verification |
| Rush Part Orders | Sourcing mistakes | Pre-approved RoHS supplier lists |
| No Functional Test | Field failures | Optional test fixture dev in 48h |
You want fast? We offer 72-hour turnaround with lead-free RoHS compliance—and we’ll still sleep at night.
🧩 Is Lead-Free Always the Better Choice? Common Pain Points and Our Solutions
Let’s be real: lead-free solder isn’t perfect.
🛠️ Common Industry Pain Points:
-
“Why are my boards delaminating more often?”
-
“Why does our AOI keep flagging false rejects?”
-
“Why do prototype joints look worse than final batch?”
🧪 Our Solutions:
-
Temperature profiling per panel instead of per job.
-
Custom fixture design for uneven board topologies.
-
IPC-trained QA engineers spot real issues—not cosmetic variances.
So… is lead solder banned in electronics? For consumer goods and EU markets—yes. For military or aerospace? Not always. But designing with RoHS-compliant assembly from the start avoids rework and redesign.
FAQs
1. Can you use 60/40 solder for electronics instead of lead-free solder?
Yes, 60/40 solder (tin/lead) is still used in some non-RoHS applications because of its excellent wetting and lower melting point (around 188°C). However, it’s not allowed in RoHS-compliant PCB assembly, especially for consumer or export electronics. If you're targeting global markets, lead-free solder PCB manufacturing is the safer, regulation-ready option—even if it requires a higher reflow temperature.
2. Is 63/37 solder better than 60/40 for electronics assembly?
Technically, yes. 63/37 solder is a eutectic alloy, meaning it transitions directly from solid to liquid at 183°C—ideal for minimizing cold joints. While it's more stable than 60/40 solder, both are leaded and therefore non-compliant with RoHS standards. For modern designs requiring RoHS-compliant PCB assembly, lead-free options like SAC305 are preferred, even with their higher melting points.
3. What’s the difference between 50/50 solder and 60/40 solder—and can I use either for electronics?
50/50 solder contains equal parts tin and lead, melts at around 215°C, and is generally used in plumbing, not electronics. It lacks the smooth flow and electrical performance needed for PCB work. On the other hand, 60/40 solder melts more easily and offers better conductivity. But for lead-free solder PCB manufacturing, neither is suitable—use SAC305 or other RoHS-approved alloys.
4. How can I improve solder joint strength with lead-free solder?
Lead-free joints can be less ductile, but strength and reliability can be improved with:
Correct reflow profile for lead-free solder
Good pad design and surface finish
Using a high-quality lead-free solder paste
Avoiding excessive thermal cycles
Also, joints can be reinforced using underfill or selective soldering techniques. A well-tuned lead-free process can match or even exceed the durability of traditional leaded joints.
Have Specific Requirements?
Looking for high-precision PCB assembly for your products? Our team specializes in delivering top-tier assembly services, ensuring your devices perform flawlessly in any environment. Contact us today for a free consultation on how we can enhance your product’s reliability.
🔚 Summary
Switching to lead-free solder isn’t just a checkbox—it changes how your entire assembly behaves. If you’re tired of trial-and-error and want precision and predictability, let’s talk. We’ll show you how we make lead-free PCB manufacturing work at every level—speed, cost, and quality.
Save on your next PCB project?
Claim $100 OFF your order today.
✅ high-quality PCB assembly with strict quality control ✅ ISO-certified & 8+ years of experience. ✅ Low MOQ, fast turnaround, and 100% E-tested PCBs.
Additional Resources:
- How to Repair Circuit Boards: A Step-by-Step Beginner’s Guide
- Capacitor on Circuit Board: A Comprehensive Guide
- What Are PCB Conformal Coatings? Types, Benefits, and Applications Explained
- SMD Size Codes Explained: A Complete Guide to Understanding Surface-Mount Component Dimensions
- AC vs DC: Key Differences, Applications, and Advantages in Modern Electronics
Request for Quote
RECENT POSTS

PCB Transformer Explained: Types, Working Principle, and Design Tips
Discover how PCB transformers work, their key types, and design integration tips. Learn to select
Why Smart OEMs Avoid Cheap PCB Assembly: 5 Hidden Risks That Cost More
Avoid costly mistakes in OEM projects. Discover why cheap PCB assembly risks quality, compliance, and
RELATED POSTS
Leading PCBA Manufacturer
✅ Assemble 20 PCBAS for $0 ✅ Get $100 OFF – Risk-Free Trial!
✅ 100+ Satisfied Customers
✅ Ensured Quality & On-Time Delivery
✅ Free Trial, No Commitments!




